Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the expression of integrated rate equation for zero order reaction.
Solution
The integrated rate equation for zero-order reaction is k = `([R_0 - R])/t`
Where,
k = Rate constant
R0 = Initial concentration of reactant
R = Final concentration of reactant
t = Time taken
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The reaction between A and B is first order with respect to A and zero order with respect to B. Fill in the blanks in the following table:
| Experiment | A/mol L−1 | B/mol L−1 | Initial rate/mol L−1 min−1 |
| I | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| II | ______ | 0.2 | 4.0 × 10−2 |
| III | 0.4 | 0.4 | ______ |
| IV | ______ | 0.2 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
For which of the following reaction the units of rate constant and rate of the reaction are same?
Which of the following graphs is correct for a zero order reaction?
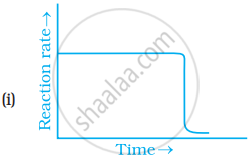
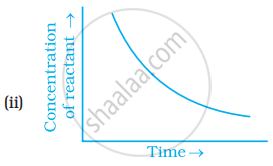
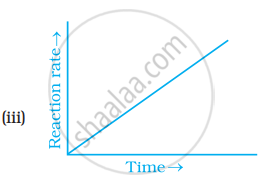

Derive an expression to calculate time required for completion of zero order reaction.
For a zero order reaction will the molecularity be equal to zero? Explain.
Consider the following statement:-
(i) Increase in concentration of reactant increases the rate of a zero-order reaction.
(ii) Rate constant k is equal to collision frequency A if Ea = 0
(iii) Rate constant k is equal to collision frequency A if Ea = 0
(iv) In k vs t is a straight line
(v) In k vs 1/T is a straight line
Which of the above statement is correct?
For a zero-order reaction, the plot of [A]t vs t is linear with a ______
Assertion (A): For a zero-order reaction, the unit of rate constant and rate of reaction are same.
Reason (R): Rate of reaction for zero order reaction is independent of concentration of reactant.
What is zeroth order reaction? Derive its integrated rate Law. What are the units of rate constant?
What is zero order reaction?
