Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2021-2022
Date & Time: 7th May 2022, 10:30 am
Duration: 2h
Advertisements
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- This question paper contains 12 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper comprises of three sections - Sections A, B, and C.
- Section A - Q. No. 1 to 3 are very short-answer type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- Section B - Q. No. 4 to 11 are short-answer type questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C - Q. No 12 is a case-based question carrying 5 marks.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Write the expression of integrated rate equation for zero order reaction.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their property indicated:
Ethanal, Propanone, Propanal, Butanone (reactivity towards nucleophilic addition)
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their property indicated:
4-Nitrobenzoic acid, benzoic acid, 3,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxy benzoic acid (Acid strength)
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Explain the following reactions:
Wolff Kishner reduction
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Explain the following reaction:
Cannizzaro reaction
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Observe the graph shown in figure and answer the following questions:
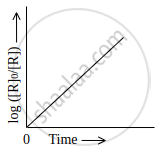
- What is the order of the reaction?
- What is the slope of the curve?
- Write the relationship between k and t1/2 (half life period).
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Write the IUPAC name of the following complex:
K2[PdCl4]
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Using crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d5 ion, if Δ0 > P.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
What are Homoleptic complexes?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Advertisements
Why chelate complexes are more stable than complexes with unidentate ligands?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
What is the spectrochemical series?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
What is the difference between a weak field ligand and a strong field ligand?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
State Hardy-Schulze rule.
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
What is Electrophoresis?
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Write three differences between Physisorption and Chemisorption.
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Write any two consequences of Lanthanoid Contraction.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Name the element of 3d series which exhibits the largest number of oxidation states. Give reason.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Give reasons for the following statement:
Copper does not displace hydrogen from acids.
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Give reasons for the following statement:
Transition metals and most of their compounds show paramagnetic behaviour.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Give reasons for the following statement:
\[\ce{Zn}\], \[\ce{Cd}\] and \[\ce{Hg}\] are soft metals.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Advertisements
Account for the following:
pKb of aniline is more than that of methylamine.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons for the following:
Aniline does not undergo Friedel- Crafts reaction.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reason for the following:
Primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Account for the following:
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their basic strength in aqueous solution: CH3NH2,(CH3)3N,(CH3)2NH
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
What is the role of pyridine in the acylation reaction of amines?
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
A compound 'A' on reduction with iron scrap and hydrochloric acid gives compound 'B' with molecular formula C6H7N. Compound 'B' on reaction with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH produces an obnoxious smell of carbylamine due to the formation of 'C'. Identify 'A', 'B' and 'C' and write the chemical reactions involved.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Complete the following:
\[\ce{CH3CN ->[1. AlH(i - Bu)2][2. H2O] 'A' ->[H2N-OH][H^+] 'B'}\]
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
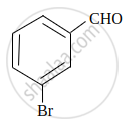
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write chemical test to distinguish between the following compounds:
Phenol and Benzoic acid
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Convert the following:
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Convert the following:
Propan-1-ol to 2-Bromopropanoic acid
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Convert the following:
Acetaldehyde to But-2-enal
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
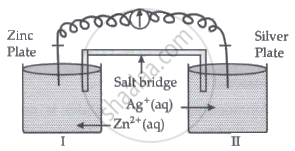
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
|
Oxidation-reduction reactions are commonly known as redox reactions. They involve transfer of electrons from one species to another. In a spontaneous reaction, energy is released which can be used to do useful work. The reaction is split into two half-reactions. Two different containers are used and a wire is used to drive the electrons from one side to the other and a Voltaic/Galvanic cell is created. It is an electrochemical cell that uses spontaneous redox reactions to generate electricity. A salt bridge also connects to the half-cells. The reading of the voltmeter gives the cell voltage or cell potential or electromotive force. If \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] is positive the reaction is spontaneous and if it is negative the reaction is non-spontaneous and is referred to as electrolytic cell. Electrolysis refers to the decomposition of a substance by an electric current. One mole of electric charge when passed through a cell will discharge half a mole of a divalent metal ion such as Cu2+. This was first formulated by Faraday in the form of laws of electrolysis.
|
- Is silver plate the anode or cathode? (1)
- What will happen if the salt bridge is removed? (1)
- When does electrochemical cell behaves like an electrolytic cell? (1)
- (i) What will happen to the concentration of Zn2+ and Ag+ when Ecell = 0. (1)
(ii) Why does conductivity of a solution decreases with dilution? (1)
OR
The molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm2mol-1. Calculate the conductivity of this solution. (2)
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2021 - 2022
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2022 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.