Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Derive the equation : W = - PextAV
Solution
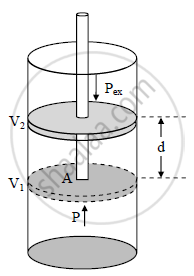
- The work W, that is done due to the expansion or compression of a gas against an external opposing pressure P is called pressure-volume work.
- Consider a certain amount of gas at pressure P, volume V1 and temperature T enclosed in a cylinder fitted with frictionless, rigid, movable piston of area A as shown in the figure.
- As the gas expands, it pushes the piston upward through a distance d against an external opposing force f. The work done by the gas during the process is given by,
W = opposing force × distance = -f.d ....(1) - The negative sign signifies that when the piston moves against an opposing force, the internal energy of the system doing the work will decrease. The force opposing the expansion is the constant external pressure, pex multiplied by the area A of the piston.
f = pex . A ....(2)
From equations (1) and (2),
W = -pex × A × d - The product A.d is the volume of the cylinder covered by the piston during its motion that is the change in volume during expansion. Thus
A × d = ΔV = V2 - V1
where, V2 is the final volume of the gas.
W = -pex ⋅ ΔV = -pex (V2 - V1)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Absolute entropies of solids, liquids and gases can be determined by
- Measuring heat capacity of substance at various temperatures
- Subtracting standard entropy of reactants from products
- Measuring vibrational motion of molecules
- Using formula ΔS° = ST° - SO°
Determine whether the reactions with the following ΔH and ΔS values are spontaneous or non-spontaneous. State whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
(a) ΔH = -110kJ, ΔS = + 40JK-1 at 400 K
(b) ΔH = + 40kJ, ΔS = -120JK-1 at 250K
300 M mol of perfect gas occupies 13 L at 320 K. Calculate the work done in joules when the gas expands-
(a) isothermally against a Constant external pressure of 0.20atm.
(b) isothermal and reversible process.
(c) into vaccum until the volume of gas is increased by 3L (R=8.314J mol-1 K-1)
One mole of a gas expands by 3L against a constant pressure of 3 atmosphere. Calculate the work done in -
(a) L.atmosphere
(b) Joules
(c) Calories
Which of the following pairs is an intensive property?
(A) Density, viscosity
(B) Surface tension, mass
(C) Viscosity, internal energy
(D) Heat capacity, volume
55 L atm of work is obtained when 1.0 mole of an ideal gas is compressed isothermally from
a volume of 28.5 L to 18.5 L, the constant external pressure is
(A) 5.05 atm
(B) 5.5 atm
(C) 0.05 atm
(D) 0.55 atm
For a certain reaction, ∆H = − 50 kJ and ∆S = − 80 J K-1, at what temperature does the
reaction turn from spontaneous to non-spontaneous?
(A) 6.25 K
(B) 62.5 K
(C) 625 K
(D) 6250 K
What is the action of heat on potassium permanganate?
5 moles of helium expand isothermally and reversibly from a pressure 40 × 10-5 N m-2 to 4 × 10-5 N m-2 at 300 K. Calculate the work done, change in internal energy and heat absorbed during the expansion. (R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1).
