Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Despite their - I effect, halogens are o- and p-directing in haloarenes. Explain.
Solution
In case of aryl halides, halogens are little deactivating because of their strong -I effect. Therefore, overall electron density on the benzene ring decreases. In other words, halogens are deactivating due to -I effect. However, because of the +R-effect, i.e., participation of lone pairs of electrons on the halogen atom with the π-electrons of the benzene ring, the electron density increases more at o- and p-positions than at m-positions.
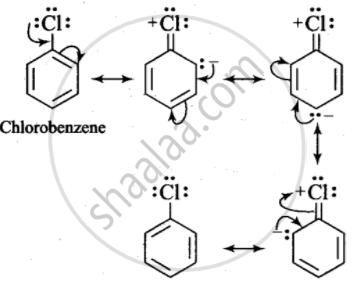
As a result, halogens are o-, p-directing. The combined result of +R-effect and -I-effect of halogens is that halogens are deactivating but o, p-directing.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Arrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give reason for this behaviour.
Suggest a route to prepare ethyl hydrogensulphate (CH3 – CH2 – OSO2 – OH) starting from ethanol (C2H5OH).
Which of the following decolourizes \[\ce{KMnO4}\] (neutral or slightly alkaline)?
Lindlar's catalyst is used for controlled:
An alkene ‘A’ contains three C – C, eight C – H σ bonds and one C – C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Write IUPAC name of ‘A’.
