Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss the nature of bonding in metal carbonyls.
Solution
The metal-carbon bond in metal carbonyls possess both σ and π character. The M–C σ bond is formed by the donation of lone pair of electrons on the carbonyl carbon into a vacant orbital of the metal. The M–C π bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from a filled d orbital of metal into the vacant antibonding π* orbital of carbon monoxide. The metal to ligand bonding creates a synergic effect which strengthens the bond between CO and the metal.
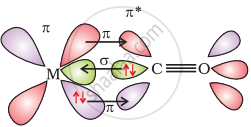
Synergic bonding
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C4H8O. Isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollens' test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollens' test but gives positive Iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product (D).
1) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D).
2) Out of (A), (B), and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards the addition of HCN?
Which element in Group IV can show high catenation property?
Which of the following is not considered as organometallic compound?
What is the oxidation number of Fe in Fe(CO)5?
The effective atomic number (EAN) of a metal carbonyl, m(CO)x is 36. The atomic number of the metal is 26. The value of 'x' is ______.
