Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a schematic sketch of an ac generator describing its basic elements. State briefly its working principle. Show a plot of variation of
(i) Magnetic flux and
(ii) Alternating emf versus time generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field.
Solution
Principle − Based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Construction:

Main parts of an ac generator:
Armature − The rectangular coil ABCD
Filed Magnets − Two pole pieces of a strong electromagnet
Slip Rings − The ends of the coil ABCD are connected to two hollow metallic rings R1 and R2.
Brushes − B1 and B2 are two flexible metal plates or carbon rods. They are fixed and are kept in tight contact with R1 and R2, respectively.
Working − As the armature coil is rotated in the magnetic field, angle θ between the field and the normal to the coil changes continuously. Therefore, magnetic flux linked with the coil changes and an emf is induced in the coil. According to Fleming’s right hand rule, current is induced from A to B in AB and from C to D in CD. In the external circuit, current flows from B2 to B1.
To calculate the magnitude of emf induced:
Suppose A → Area of each turn of the coil
N → Number of turns in the coil
`vecB`→ Strength of the magnetic field
θ → Angle which normal to the coil makes with `vecB` at any instant t
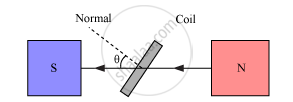
∴ Magnetic flux linked with the coil in this position is given by,
`phi=N(vecB.vecA)=NBAcostheta=NBAcos `
Where, ‘ω’ is angular velocity of the coil
Graph between magnetic flux and time, according to equation (i), is shown below:

As the coil rotates, angle θ changes. Therefore, magnetic flux Φ linked with the coil changes and an emf is induced in the coil. At this instant t, if e is the emf induced in the coil, then
`e=(dtheta)/dt=-d/dt(NABcos`
`=-NABd/dt(cos `
=-NAB(-sin ωt)ω
∴ e = NAB ω sin ωt
The graph between alternating emf versus time is shown below:

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1.5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
A metallic loop is placed in a nonuniform magnetic field. Will an emf be induced in the loop?
Calculate magnetic flux density of the magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil of 50 turns, having a radius of 0.5m and carrying a current of 5 A.
Whenever the magnetic flux linked with an electric circuit changes, an emf is induced in the circuit. This is called ______.
The dimensions of magnetic flux are ______
Consider a closed loop C in a magnetic field (Figure). The flux passing through the loop is defined by choosing a surface whose edge coincides with the loop and using the formula φ = B1.dA1 + B2.dA2 +... Now if we chose two different surfaces S1 and S2 having C as their edge, would we get the same answer for flux. Jusity your answer.
A coil is placed in a time varying magnetic field. If the number of turns in the coil were to be halved and the radius of wire doubled, the electrical power dissipated due to the current induced in the coil would be: (Assume the coil to be short circuited.)
A circular coil of 1000 turns each with area 1 m2 is rotated about its vertical diameter at the rate of one revolution per second in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.07T. The maximum voltage generation will be ______ V.
The Figure below shows an infinitely long metallic wire YY' which is carrying a current I'.
P is a point at a perpendicular distance r from it.
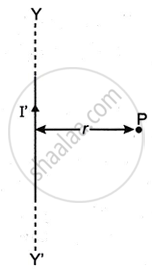
- What is the direction of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- What is the magnitude of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- Another metallic wire MN having length l and carrying a current I is now kept at point P. If the two wires are in vacuum and parallel to each other, how much force acts on the wire MN due to the current I' flowing in the wire YY'?
