Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Draw the geometrical isomers of complex \[\ce{[Pt(en)2Cl2]^2+}\].
Draw the geometrical isomers of the given complex:
\[\ce{[Pt(en)2Cl2]^2+}\]
Solution 1
Geometrical isomers of complex\[\ce{[Pt(en)2Cl2]^2+}\]
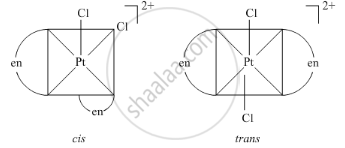
Solution 2
Geometrical isomers of Dichloridobisethane-1, 2-diammine platinum (iv) ion
 |
 |
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw one of the geometrical isomers of the complex [Pt (en)2Cl2] +2 which is optically inactive
Draw the structure of optical isomers of [PtCl2(en)2]2+.
Draw the structure of optical isomers of [Cr(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+.
Write the structures of optical isomers of the complex ion `[Co(en)_2Cl_2]^+`
What type of structural isomers are [Co(NH3)5 Br] SO4 and [Co(NH3)5 SO4]Br? Give a chemical test to distinguish the isomers.
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pairs of compound:
(1) (C2H5)2NH and CH3-NH-C3H7
(2) 1 – butanol and 2 methyl-1 -propanol.
Name the type of isomerism that the compound with molecular formula C3H6O2 exhibits. Represent the isomers.
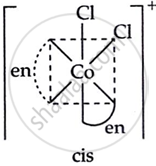
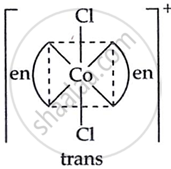
Draw the geometrical isomers of [Co(en)2Cl2]2+. Which geometrical isomer of [Co(en)2Cl2]2+ is not optically active and why?
Which of the following molecules has a chiral centre correctly labelled with an asterisk (*)?
Assertion: Addition of bromine water to 1-butene gives two optical isomers.
Reason: The product formed contains two asymmetric carbon atoms.
