Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Estimate the total number of air molecules in a room of a capacity of 25 m3 at a temperature of 27°C.
Solution
T = 27°C + 273 = 300 K
kB = 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1
V = 25 m3
As Boltzmann’s Constant, kB = `"R"/"N"` ⇒ R = kBN
Now, PV = nRT = nkBNT
The number of molecules in the room,
nN = `"PV"/("k"_"B""T") = (1.013 xx 10^5 xx 25)/(1.38 xx 10^-23 xx 300)`
= `(25.325 xx 10^5)/(414 xx 10^-23)`
= 0.06117 × 1028
= 6.117 × 1026 molecules
nN = 6.1 × 1026 molecules
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the kinetic energy of 3 litre of gas at S.T.P given standard pressure is 1.013 × 105 N/m2.
Two identically sized rooms A and B are connected by an open door. If the room A is air-conditioned such that its temperature is 4°C lesser than room B, which room has more air in it?
The ratio γ = `"C"_"p"/"C"_"v"` for a gas mixture consisting of 8 g of helium and 16 g of oxygen is ____________.
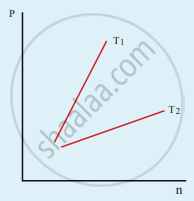
The following graph represents the pressure versus number density for an ideal gas at two different temperatures T1 and T2. The graph implies
If 1020 oxygen molecules per second strike 4 cm2 of wall at an angle of 30° with the normal when moving at a speed of 2 × 103 ms−1, find the pressure exerted on the wall. (mass of one oxygen atom = 2.67 × 10−26 kg)
A perfect gas of 'N' molecules, each of mass 'm', moving with velocities 'C1', 'C2', ...... .'CN' is enclosed in a cubical vessel of volume 'V'. The pressure exerted by the gas on the walls of the vessel is ______. ('p' = density of gas)
The average force applied on the walls of a closed container depends as 'Tx', where 'T' is the temperature of an ideal gas. The value of 'x' is ______.
Does an ideal gas exist in practice?
The kinetic energy per molecule of a gas at temperature T is ______.
Temperature remaining constant, if you double the number of molecules in a box, the pressure will ______.
