Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain. Aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Solution
- The low reactivity of aryl halides is due to the resonance effect and sp2 hybrid state of carbon to which halogen atom is attached.
- In aryl halides, one of the lone pairs of electrons on the halogen atom is in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring. Due to resonance, the C–X bond acquires partial double bond character. Thus, the C–X bond in aryl halides is stronger and shorter than alkyl halides. Hence, it is difficult to break C–X bond in aryl halides.
- Further, the phenyl cation produced due to the self-ionization of aryl halide will not be stabilised by resonance. This rules out the possibility of SN1 mechanism. Also, the backside attack of nucleophiles is blocked by the aromatic ring. This rules out the possibility of SN2 mechanism. As a result, nucleophilic substitution reaction involving cleavage of C–X bond in haloarenes proceeds with difficulty.
- Therefore, aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
RELATED QUESTIONS
from the following pair would undergo SN2 faster from the other?
a. CH3CH2CH2I b. CH3CH2CH2Cl
Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
Chlorobenzene to biphenyl
Distinguish between SN1 and SN2 mechanism of substitution reaction.
Convert the following:
Propene to propan-1-ol
Convert the following:
Benzyl alcohol to benzyl cyanide
Propane nitrile can be prepared by heating ____________
Major product of the following reaction is _______________
\[\ce{CH3-CH2-Mg-Br + NH3 ->?}\]
Which of the following is a primary halide?
The least reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions is ____________.
Ethyl bromide undergoes the following reaction:
\[\ce{\underset{Ethyl bromide}{C2H5Br} + \underset{(aq.)}{KOH} ->[\Delta] \underset{Ethyl alcohol}{C2H5OH} + KBr}\]
Which of the following is a WRONG statement?
Nitroalkanes are obtained in laboratory from primary or secondary alkyl halides by the action of ______.
The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction of NO2 with F2 to form NO2F:
\[\ce{NO2_{(g)} + F2_{(g)} -> NO2F_{(g)} + F_{(g)} (slow)}\]
\[\ce{F_{(g)} + NO2_{(g)} -> NO2F_{(g)} (fast)}\]
The order of the reaction with respect to NO2(g)
What type of hybridisation is present in carbocation formed during the alkaline hydrolysis of 1- bromo-1- phenyl ethane?
\[\ce{C6H5CH2Cl + KCN(alc) -> X + Y}\]
Compounds X and Y are ____________.
Which of the following carbocation is the most stable?
Identify major product 'B' in the following reaction.
\[\ce{But-1-ene ->[HBr][Peroxide] A ->[AgCN][\Delta] B}\]
The order of reactivity of the given haloalkanes towards nucleophiles is:
Which among the following statements is not correct about SN2 reaction mechanism?
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}\\
|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3 - c - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether]}\\
|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}
\end{array}\]
Observe the following and answer the question given below:
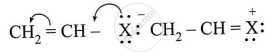
Comment on the bond length of C-X bond in it.
Discuss β - elimination reaction.
Complete the following reaction sequences by writing the structural formulae of the organic compounds 'A', 'B' and 'C'.
\[\ce{2-Bromobutan ->[alc. KOH] A ->[][Br2] B ->[][NANH2] C}\]
Complete the following reaction, giving a major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}
\end{array}\]
Identify the chiral molecule from the following.
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{...............}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether]A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}
\end{array}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl->[Na/ dry ether]A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
\end{array}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
\end{array}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
\end{array}\]
