Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain briefly:
Restriction enzymes and DNA
Solution
Restriction enzymes are used to break up DNA molecules. They are part of a broader enzyme class known as nucleases. Restriction enzymes are classified into three types: exonucleases, endonucleases, and restriction endonucleases.
- Exonucleases: They remove nucleotides from the terminal ends (5' or 3') of one double strand of DNA.
- Endonucleases: They make cuts at specific positions within the DNA. These enzymes don't fragment the ends and only affect one strand of the DNA helix.
- Restriction endonucleases: Arber identified them in bacteria in 1963. They function as "molecular scissors" or chemical scalpels. They detect the base sequence at palindrome sites in DNA sequences and sever the strands. There are three types of restriction endonucleases: type I, type II, and type III. Only type II restriction enzymes are utilised in recombinant DNA technology because they can recognise and cut inside a specified DNA sequence, typically consisting of 4 to 8 nucleotides.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are 'sticky ends' formed on a DNA strand? Why are they so called?
Mention the difference in the mode of action of exonuclease and endonuclease.
How does a restriction nuclease function? Explain
Name and describe the technique that helps in separating the DNA fragments formed by the use of restriction endonuclease
Make a chart (with diagrammatic representation) showing a restriction enzyme, the substrate DNA on which it acts, the site at which it cuts DNA and the product it produces.
Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
Collect 5 examples of palindromic DNA sequences. Better try to create a palindromic sequence by following base-pair rules.
There is a restriction endonudease called as EcoRI. What does co part in it stands for?
A specific recognition sequence identified by endonucleases to make cuts at specific positions within the DNA is ______
The role of DNA ligase in the construction of a recombinant DNA molecule is ______.
Which of the following bacteria is not a source of restriction endonuclease?
Would you choose an exonuclease while producing a recombinant DNA molecule?
Restriction enzymes should not have more than one site of action in the cloning site of a vector. Comment.
A plasmid DNA and a linear DNA (both are of the same size) have one site for a restriction endonuclease. When cut and separated on agarose gel electrophoresis, plasmid shows one DNA band while linear DNA shows two fragments. Explain.
How does one visualise DNA on an agarose gel?
Carefully observe the given picture. A mixture of DNA with fragments ranging from 200 base pairs to 2500 base pairs was electrophoresed on agarose gel with the following arrangement.
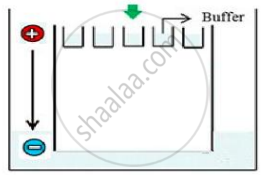
(a) What result will be obtained on staining with ethidium bromide? Explain with reason.
(b) The above setup was modified and a band with 250 base pairs was obtained at X.
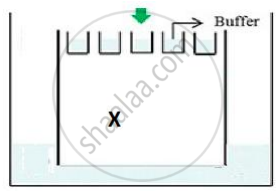
What change(s) were made to the previous design to obtain a band at X? Why did the band appear at position X?
Given below is the restriction site of a restriction endonuclease Pst-I and the cleavage sites on a DNA molecule.
\[\ce{5' C - T - G - C - A \overset{\downarrow}{-}{G 3'}}\]
\[\ce{3' G\underset{\uparrow}{-} A - C - G - T - C 5'}\]
Choose the option that gives the correct resultant fragments by the action of the enzyme Pst-I.
State the principle involved in separation of DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis.
