Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Make a chart (with diagrammatic representation) showing a restriction enzyme, the substrate DNA on which it acts, the site at which it cuts DNA and the product it produces.
Solution
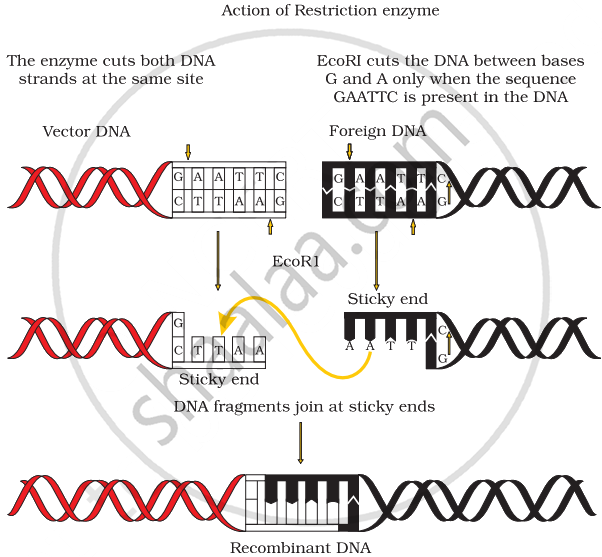
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are 'sticky ends' formed on a DNA strand? Why are they so called?
Mention the difference in the mode of action of exonuclease and endonuclease.
How does a restriction nuclease function? Explain
Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
Explain briefly:
Restriction enzymes and DNA
Distinguish between exonuclease and endonuclease
How does restriction endonuclease function?
Explain the roles of the following with the help of an example each in recombinant DNA technology :
Restriction Enzymes
Answer the following question.
Explain the significance of palindromic nucleotide sequence in the formation of recombinant DNA.
Give a reason why :
Single cloning site is preferred in a vector.
A mixture containing DNA fragments a, b, c and d, with molecular weights of a + b = c, a > b and d > c was subject to agarose get electrophoresis. This position of these fragments from cathode to anode to anode sides of the gel would be ______.
Restriction enzymes ______.
In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA molecules are separated on the basis of their ______.
The role of DNA ligase in the construction of a recombinant DNA molecule is ______.
Which of the following statements does not hold true for restriction enzyme?
Given below is the stepwise schematic representation of the process of electrophoresis. Identify the 'alphabets' representing
- Anode end
- smallest/lightest DNA strand in the matrix
- Agarose gel

State the importance of elution in this process.
How are DNA fragments visualised once they are separated by gel electrophoresis?
