Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain primary benzylic halide shows higher reactivity by SN1 mechanism than other primary alkyl halide.
Solution
- SN1 reaction involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate. The benzylic carbocation intermediate formed are resonance stabilized, and hence SN1 mechanism is favoured.
- Resonance stabilization of benzylic carbocation can be represented as:

- Reactivity order of alkyl halides towards SN1 mechanism is 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3X. That is, SN1 mechanism is least favoured in primary alkyl halides.
- Benzylic carbocation formed is more stable than the primary carbocation; therefore, primary benzylic halide shows higher reactivity by SN1 mechanism than other primary alkyl halide.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
from the following pair would undergo SN2 faster from the other?
a. CH3CH2CH2I b. CH3CH2CH2Cl
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 ->[HBr][peroxide] A ->[alc. KOH] B}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3\phantom{................}}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3\phantom{................}}
\end{array}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major products.

Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
1-Chloropropane to 1-nitropropane
Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
Chlorobenzene to biphenyl
Convert the following:
Benzyl alcohol to benzyl cyanide
Convert the following:
tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide
HCl is added to a hydrocarbon ‘A’ \[\ce{(C4H8)}\] to give a compound ‘B’ which on hydrolysis with aqueous alkali forms tertiary alcohol ‘C’ \[\ce{(C4H10O)}\]. Identify ‘A’ ,‘B’ and ‘C’.
Which of the following is a primary halide?
The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction of NO2 with F2 to form NO2F:
\[\ce{NO2_{(g)} + F2_{(g)} -> NO2F_{(g)} + F_{(g)} (slow)}\]
\[\ce{F_{(g)} + NO2_{(g)} -> NO2F_{(g)} (fast)}\]
The order of the reaction with respect to NO2(g)
How many metameric ethers are represented by the molecular formula C4H10O?
Which one is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction?
What type of hybridisation is present in carbocation formed during the alkaline hydrolysis of 1- bromo-1- phenyl ethane?
Which of the following carbocation is the most stable?
Identify major product 'B' in the following reaction.
\[\ce{But-1-ene ->[HBr][Peroxide] A ->[AgCN][\Delta] B}\]
What is the major product obtained in the sulphonation of chlorobenzene with concentrated sulphuric acid?
Convert the following.
p-Nitrochlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the dehydrohalogenation of alkenes?
Complete the following reaction giving a major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl->[Na/dry ether]A}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}
\end{array}\]
Observe the following and answer the questions given below:
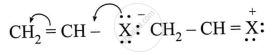
Name the type of halogen derivative.
Observe the following and answer the question given below:
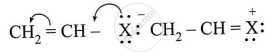
Comment on the bond length of C-X bond in it.
Discuss β - elimination reaction.
Complete the following reaction sequences by writing the structural formulae of the organic compounds 'A', 'B' and 'C'.
\[\ce{2-Bromobutan ->[alc. KOH] A ->[][Br2] B ->[][NANH2] C}\]
Complete the reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Cl ->[AgCN][alc.\Delta]}\] ?
Complete the following reaction, giving a major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}
\end{array}\]
