Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain the laws of perceptual organization.
Answer the following questions with the help of the given points:
Explain the laws of perceptual organization.
Points:
- Law of proximity
- Law of similarity
- Law of continuity
- Law of closure
Answer the following question in 80 to 100 words with the help of the given points:
Explain the laws of perceptual organization.
Points:
- Law of proximity
- Law of similarity
- Law of continuity
- Law of closure
Solution 1
Laws of Perceptual Organisation: Perception is defined as the process of assigning meaning to information received about the environment based on past experiences. Our brain has a proclivity to organize our sensations into meaningful wholes.
- Law of proximity: According to this law, the stimuli that are near each other are perceived together than the stimuli that are far away from each other.
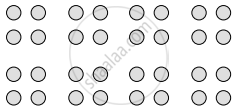
In the above image, we perceive pairs of dots in each line as the dots which are near to each other are perceived together. So, instead of perceiving a line of eight dots, generally, a line of four pairs of dots is perceived. - Law of similarity: According to this law, the stimuli that are similar to each other are perceived together than stimuli that are distinct from each other.
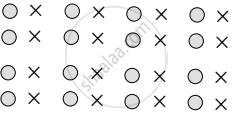
In the above image, we perceive four alternate vertical lines of circles and crosses since similar stimuli are perceived together. Generally, we do not perceive four horizontal lines with circles and crosses in alternate sequences. - Law of continuity: According to this law, there is a tendency to perceive a stimulus in continuation as per its established direction. Also, when two stimuli intersect, a continuation of each stimulus is perceived apparently.
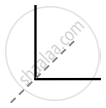
In the above image, a straight vertical line and a straight horizontal line are perceived together as a letter ‘L’, and a cutting line is perceived separately. Generally, we do not perceive four different lines going in different directions. - Law of closure: According to this law, there is a tendency to perceive an incomplete stimulus in a complete manner.

In the above image, our brain fills up gaps in incomplete stimulus and we perceive it as a triangle and square. Generally, we do not perceive it as three/four separate lines going in different directions.
Solution 2
Laws of Perceptual Organisation: Perception is defined as the process of assigning meaning to information received about the environment based on past experiences. Our brain has a proclivity to organize our sensations into meaningful wholes.
- Law of proximity: According to this law, the stimuli that are near each other are perceived together than the stimuli that are far away from each other.
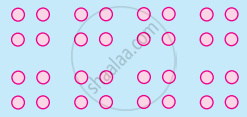
In the above image, we perceive pairs of dots in each line as the dots which are near to each other are perceived together. So, instead of perceiving a line of eight dots, generally, a line of four pairs of dots is perceived. - Law of similarity: According to this law, the stimuli that are similar to each other are perceived together than stimuli that are distinct from each other.

In the above image, we perceive four alternate vertical lines of circles and crosses since similar stimuli are perceived together. Generally, we do not perceive four horizontal lines with circles and crosses in alternate sequences. - Law of continuity: According to this law, there is a tendency to perceive a stimulus in continuation as per its established direction. Also, when two stimuli intersect, a continuation of each stimulus is perceived apparently.
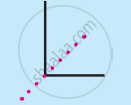
In the above image, a straight vertical line and a straight horizontal line are perceived together as a letter ‘L’, and a cutting line is perceived separately. Generally, we do not perceive four different lines going in different directions. - Law of closure: According to this law, there is a tendency to perceive an incomplete stimulus in a complete manner.
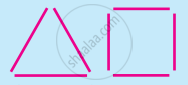
In the above image, our brain fills up gaps in incomplete stimulus and we perceive it as a triangle and square. Generally, we do not perceive it as three/four separate lines going in different directions.
Notes
Students should refer to the answer according to their questions.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question in 25 to 30 words:
Explain the law of proximity in perception.
Max Wertheimer gave laws of perception.
Write short note in 50 to 60 words.
Types of perceptual processing
Explain the following concept in 25 to 30 words.
Top-down processing
Answer the following question in 25 to 30 words.
What is law of proximity?
