Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figure shows a person standing somewhere in between two identical tuning forks. each vibrating at 512 Hz. If both the tuning forks move towards right a speed of 5.5 m s−1, find the number of beats heard by the listener. Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.

Solution
Given:
Frequency of tuning forks \[f_0\]= 512 Hz
Speed of sound in air v = 330 ms−1
Velocity of tuning forks \[v_s\]= 5.5 ms−1
The apparent frequency \[\left( f_1 \right)\] heard by the person from the tuning fork on the left is given by:
\[f_1 = \left( \frac{v}{v + v_s} \right) \times f_0\]
On substituting the values in the above equation, we get:
\[f_1 = \left( \frac{330}{330 + 55} \right) \times 512\]
\[ = 503 . 60 \text { Hz }\]
Similarly, apparent frequency \[\left( f_2 \right)\] heard by the person from the tuning fork on the right is given by:
\[f_2 = \left( \frac{v}{v - v_s} \right) \times f_0\]
On substituting the values in the above equation, we get:
\[f_2 = \left( \frac{330}{330 - 5 . 5} \right) \times 512\]
\[ = 520 . 68 \text { Hz }\]
∴ beats produced
=\[f_2 - f_1\]
= 520.68 − 503.60 = 17.5 Hz
As the difference is greater than 10 (the persistence of sound for the human ear is 1/10 of a second), the sound gets overlapped, and the observer cannot distinguish between the sounds and the beats.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two waves represented by \[y = a\sin\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] and \[y = a\cos\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] \[y = a\cos\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] are superposed. The resultant wave will have an amplitude
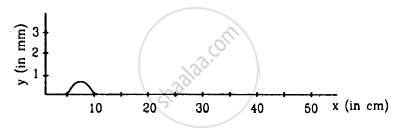
following Figure shows a wave pulse at t = 0. The pulse moves to the right with a speed of 10 cm s−1. Sketch the shape of the string at t = 1 s, 2 s and 3 s.
A wave is described by the equation \[y = \left( 1 \cdot 0 mm \right) \sin \pi\left( \frac{x}{2 \cdot 0 cm} - \frac{t}{0 \cdot 01 s} \right) .\]
(a) Find the time period and the wavelength? (b) Write the equation for the velocity of the particles. Find the speed of the particle at x = 1⋅0 cm at time t = 0⋅01 s. (c) What are the speeds of the particles at x = 3⋅0 cm, 5⋅0 cm and 7⋅0 cm at t = 0⋅01 s?
(d) What are the speeds of the particles at x = 1⋅0 cm at t = 0⋅011, 0⋅012, and 0⋅013 s?
Two audio speakers are kept some distance apart and are driven by the same amplifier system. A person is sitting at a place 6.0 m from one of the speakers and 6.4 m from the other. If the sound signal is continuously varied from 500 Hz to 5000 Hz, what are the frequencies for which there is a destructive interference at the place of the listener? Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
A cylindrical metal tube has a length of 50 cm and is open at both ends. Find the frequencies between 1000 Hz and 2000 Hz at which the air column in the tube can resonate. Speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1.
In a resonance column experiment, a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm and the second resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 62.0 cm. (a) Find the speed of sound in air. (b) How much distance above the open end does the pressure node form?
A U-tube having unequal arm-lengths has water in it. A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz can set up the air in the shorter arm in its fundamental mode of vibration and the same tuning fork can set up the air in the longer arm in its first overtone vibration. Find the length of the air columns. Neglect any end effect and assume that the speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A Kundt's tube apparatus has a copper rod of length 1.0 m clamped at 25 cm from one of the ends. The tube contains air in which the speed of sound is 340 m s−1. The powder collects in heaps separated by a distance of 5.0 cm. Find the speed of sound waves in copper.
A Kundt's tube apparatus has a steel rod of length 1.0 m clamped at the centre. It is vibrated in its fundamental mode at a frequency of 2600 Hz. The lycopodium powder dispersed in the tube collects into heaps separated by 6.5 cm. Calculate the speed of sound in steel and in air.
Calculate the frequency of beats produced in air when two sources of sound are activated, one emitting a wavelength of 32 cm and the other of 32.2 cm. The speed of sound in air is 350 m s−1.
The horn of a car emits sound with a dominant frequency of 2400 Hz. What will be the apparent dominant frequency heard by a person standing on the road in front of the car if the car is approaching at 18.0 km h−1? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A bat emitting an ultrasonic wave of frequency 4.5 × 104 Hz flies at a speed of 6 m s−1between two parallel walls. Find the fractional heard by the bat and the beat frequencies heard by the bat and the beat frequency between the two. The speed of sound is 330 m s−1.
A traffic policeman sounds a whistle to stop a car-driver approaching towards him. The car-driver does not stop and takes the plea in court that because of the Doppler shift, the frequency of the whistle reaching him might have gone beyond the audible limit of 25 kHz and he did not hear it. Experiments showed that the whistle emits a sound with frequency closed to 16 kHz. Assuming that the claim of the driver is true, how fast was he driving the car? Take the speed of sound in air to be 330 m s−1. Is this speed practical with today's technology?
A car moving at 108 km h−1 finds another car in front it going in the same direction at 72 km h−1. The first car sounds a horn that has a dominant frequency of 800 Hz. What will be the apparent frequency heard by the driver in the front car? Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
Two submarines are approaching each other in a calm sea. The first submarine travels at a speed of 36 km h−1 and the other at 54 km h−1 relative to the water. The first submarine sends a sound signal (sound waves in water are also called sonar) at a frequency of 2000 Hz. (a) At what frequency is this signal received from the second submarine. At what frequency is this signal received by the first submarine. Take the speed of of the sound wave in water to be 1500 m s−1.
A source emitting a sound of frequency v is placed at a large distance from an observer. The source starts moving towards the observer with a uniform acceleration a. Find the frequency heard by the observer corresponding to the wave emitted just after the source starts. The speed of sound in the medium is v.
The speed of sound in hydrogen is 1270 m/s. The speed of sound in the mixture of oxygen and hydrogen in which they are mixed in 1:4 ratio is
A spring breaks under tension of 10 kg wt.If the string is used to revolve a body of mass 1.2 kg in a horizontal circle. of radius 50 cm, what is the maximum speed with which a body can be revolved?
Two tuning forks having frequencies 320 Hz and 340 Hz are sounded together to produce sound waves. The velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s. Find the difference in wavelength of these waves.
