Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the area of the quadrilateral whose vertices are A(–3, 1), B(–2, –2), C(4, 1), D(2, 3).
Solution
A(–3, 1), B(–2, –2), C(4, 1), D(2, 3)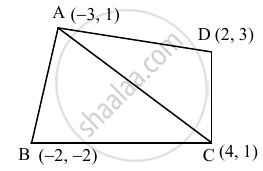
A(`square`ABCD) = A(ΔABC) + A(ΔACD)
Area of triangle = `1/2|(x_1, y_1, 1),(x_2, y_2, 1),(x_3, y_3, 1)|`
A(ΔABC) = `1/2|(-3, 1, 1),(-2, -2, 1),(4, 1, 1)|`
= `1/2[-3(-2 - 1) - 1(-2 - 4) + 1(-2 + 8)]`
= `1/2(9 + 6 + 6)`
∴ A(ΔABC) = `21/2` sq. units'.
∴ A(ΔACD) = `1/2|(-3, 1, 1),(4, 1, 1),(2, 3, 1)|`
= `1/2[-3(1 - 3) - 1(4 - 2) + 1(12 - 2)]`
= `1/2(6 - 2 + 10)`
∴ A(ΔACD) = 7 sq. units
∴ A(`square`ABCD) = A(ΔABC) + A(ΔACD)
= `21/2 + 7`
= `35/2` sq. units.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are: (4, 5), (0, 7), (–1, 1)
Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are: (0, 5), (0, – 5), (5, 0)
Find the area of triangles whose vertices are A(−1, 2), B(2, 4), C(0, 0).
Find the area of triangles whose vertices are P(3, 6), Q(−1, 3), R(2, −1)
Find the value of k, if area of ΔPQR is 4 square units and vertices are P(k, 0), Q(4, 0), R(0, 2).
Find the value of k, if area of ΔLMN is `33/2` square units and vertices are L(3, − 5), M(− 2, k), N(1, 4).
The maximum area of a right angled triangle with hypotenuse h is:
Find the values of 'K' if area of triangle is 4 square units and vertices are (k, 0), (4, 0), (0, 2).
If Δ = `|(1, 2, 3),(2, -1, 0),(3, 4, 5)|`, then `|(1, 6, 3),(4, -6, 0),(3, 12, 5)|` is
Find the area of triangle whose vertices are A ( -1,2), B (2,4), C (0,0)
Find the area of triangle whose vertices are A ( -1,2) ,B (2,4) ,C (0,0)
Find the area of triangle whose vertices are A( -1, 2), B(2, 4), C(0, 0)
Find the area of triangle whose vertices are A(-1,2), B(2,4), C(0,0)
Find the area of triangle whose vertices are A( -1, 2), B(2, 4), C(0, 0).
Find the area of triangle whose vertices are A(-1, 2), B(2, 4), C(0, 0).
Find the area of triangle whose vertices are A(-1, 2), B(2, 4), C(0, 0)
Find the area of triangle whose vertices are A(-1, 2), B(2, 4), C(0, 0).
