Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give an account of the occupational structure of India’s population.
Solution
The population of India according to their economic status is divided into three groups, namely; main workers, marginal workers, and non-workers. It is observed that in India, the proportion of workers (both main and marginal) is only 39 percent (2001) leaving a vast majority of 61 percent as non-workers. This indicates an economic status in which there is a larger proportion of the dependent population, further indicating the possible existence of a large number of unemployed or under-employed people.
The occupational composition of India’s population (which actually means engagement of an individual in farming, manufacturing trade, services, or any kind of professional activities) shows a large proportion of primary sector workers compared to secondary and tertiary sectors. About 58.2 per cent of the total working population are cultivators and agricultural labourers, whereas only 4.2% of workers are engaged in household industries and 37.6% are other workers including non-household industries, trade, commerce, construction and repair and others. services. As far as the occupation of the country’s male and female population is concerned, male workers outnumber female workers in all three sectors. The number of female workers is relatively high in the primary sector, though in recent years there has been some improvement in the work participation of women in secondary and tertiary sectors.
The participation rate in secondary and tertiary sectors has registered an increase. This indicates a shift of dependence of workers from farm-based occupations to non-farm-based ones, indicating a sectoral shift in the economy of the country. The spatial variation of work participation rate in different sectors in the country is very wide. For instance, the states like Himachal Pradesh and Nagaland have very large shares of cultivators. On the other hand states like Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Madhya Pradesh have a higher proportion of agricultural labourers. The highly urbanized areas like Delhi, Chandigarh and Puducherry have a very large proportion of workers being engaged in other services.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Identify the correct co-relation:
A: Assertion; R: Reasoning
A: Increase in the dependency ratio will affect the economy.
R: Medical costs are high when there are more elderly in the population.
Write a short note on literacy rate.
Give geographical reasons:
Literacy rate of a country is an indicator of its socio-economic development.
Give a geographical reason:
Demographic dividend increases when the proportion of the working population increases.
Answer in detail:
Explain the rural and urban population structure.
Ratio of males and females in the population is ______.
Assertion: In population pyramid, a broad base indicates high number of children in a country.
Reason: Broad apex is an indicator of high number of elderly in a country.
Identify the incorrect factor
Type of age-sex pyramid:
Identify the incorrect factor
Regions having literacy more than 80%:
Identify the incorrect factor
Factors having direct relation with literacy:
Identify the incorrect factor
Pull factors of migration:
State whether right or wrong:
Literacy ratio of population is indicator of economic and social development of a country.
Observe the following graph and answer the question given below

Question:
- Which region has the highest literacy rate?
- Which region has the lowest literacy rate?
- In which region does women fare better than men in literacy rate?
- Write a concluding paragraph about the graph.
- Which is the type of graph?
Write short note
Rural-urban structure of population
‘The agricultural sector has the largest share of Indian workers.’ – Explain.
What do you understand by population composition?
Which regions have an unfavorable sex ratio towards women?
What does age-sex pyramid define?
Why is an unfavorable female sex ratio found in India and other South Asian countries?
How does the sex ratio give important information about the status of women in a country?
How is occupational structure a good indicator of levels of economic development of a nation?
“In some countries of the world, the sex ratio is unfavourable to women.” Give one reason.
Which age group forms the working population?
“The shape of the population pyramid reflects the characteristics of the population.” Support the statement with examples.
The literacy rate in India is ______.
Which one of the following country lowest sex ratio in the world?
Which one of the following reflected by Age-Sex pyramid?
Broad base of age-sex pyramid refers to ______.
The lowest sex ratio is found in ______.
In how many countries, unfavourable sex ratio is found?
Expanding population pyranrd shows.
Which type of age-sex pyramid is of Australia?
According to the UNO, how many countries have sex ratio unfavourable for females?
Which country’s population shows a constant population?
Which of the following options, represent the correct order of states according to the population?
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:
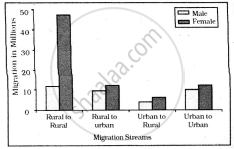
Intra-state Migration by place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
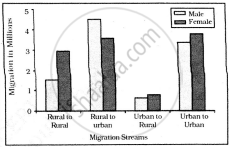
Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
What is the main cause of female migration from rural to urban?
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:

Intra-state Migration by place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011

Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
Which stream of migration shows the lowest trend in intra-state migration?
The highest sex ratio is found in:
India's population as per the 2011 census is:
Which of the following is a major concern of study about the population of a country?
The sex ratio in a country can be expressed as which of the following?
Which of the following is not a reason of unfavourable sex ratio against women?
Identify the country with the highest sex-ratio in the world.
Match the following and choose the correct option.
| Population | Pyramid shape |
| A. Constant population | 1. Perfect triangle shape |
| B. Declining population | 2. Bell shape |
| C. Expanding population | 3. Narrow Base & Tapered Top Shape |
A country having pyramid of population that has a wide base and sharply tapered top is characterised by which of the following?
Assertion: India is agrarian country.
Reason: Population engaged in agriculture is high in India.
Draw neat, labelled diagram:
Stationary pyramids
Which one of the following is the largest linguistic group of India?
Draw a neat, labelled diagram
Pyramids of underdeveloping countries.
Which one of the following is the largest linguistic group of India?
Which one of the following is the largest linguistic group of India?
