Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH ->[H2SO4][413 K] CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 + H2O}\]
Solution
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH ->[H2SO4][413 K] \underset{Diethylether}{CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3} + H2O}\]
Mechanism: The formation of ether is a nucleophilic bimolecular reaction SN2 involving the attack of alcohol molecules on protonated alcohol as below:
(1) \[\ce{CH3CH2 - \underset{\bullet\bullet}{\overset{\bullet\bullet}{O}} - H + H+ -> CH3CH2 -^+ \underset{\bullet\bullet}{\overset{\ce{H}}{\overset{\bullet\bullet}{O}}} - H}\]
(2)
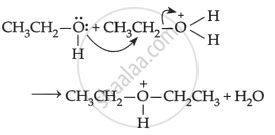
(3) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3CH2-\overset{+}{O}-CH2CH3 -> CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 + H^+}\\
|\phantom{..................................}\\
\ce{H}\phantom{..................................}
\end{array}\]
\[\ce{H^+ + HSO^Θ_4 -> H2SO4}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following is optically inactive?
Which of the following is an example of SN2 reaction?
The order of reactivity of the given haloalkanes towards nucleophile is:
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for an SN2 reaction is:
SN2 mechanism proceeds through intervention of ____________.
Why are aryl halides less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than alkyl halides? How can we enhance the reactivity of aryl halides?
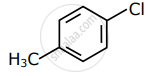
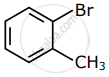
Among the following compounds I - IV, which one forms a yellow precipitate on reacting sequentially with (i) NaOH (ii) dil. HNO3 (iii) AgNO3?
 |
 |
 |
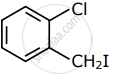 |
| I | II | III | IV |
The decreasing order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution (SN2) is ______.
Retention of configuration is observed in ______.
Acetic anhydride from acetic acid