Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH ->[H2SO4][413 K] CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 + H2O}\]
उत्तर
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH ->[H2SO4][413 K] \underset{Diethylether}{CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3} + H2O}\]
Mechanism: The formation of ether is a nucleophilic bimolecular reaction SN2 involving the attack of alcohol molecules on protonated alcohol as below:
(1) \[\ce{CH3CH2 - \underset{\bullet\bullet}{\overset{\bullet\bullet}{O}} - H + H+ -> CH3CH2 -^+ \underset{\bullet\bullet}{\overset{\ce{H}}{\overset{\bullet\bullet}{O}}} - H}\]
(2)
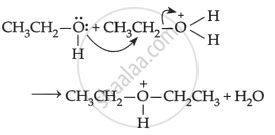
(3) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3CH2-\overset{+}{O}-CH2CH3 -> CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 + H^+}\\
|\phantom{..................................}\\
\ce{H}\phantom{..................................}
\end{array}\]
\[\ce{H^+ + HSO^Θ_4 -> H2SO4}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which compound in the following pair will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH−?
CH3Br or CH3I
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for an SN2 reaction is:
Optically active isomers but not mirror images are called ____________.
An important chemical method to resolve a racemic mixture makes use of the formation of ______.
Which of the following is a chiral compound?
The increasing order of nucleophilicity would be:
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Assertion: KCN reacts with methyl chloride to give methyl isocyanide.
Reason: CN– is an ambident nucleophile.
Inversion of configuration occurs in ______.
