Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date & Time: 28th February 2023, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully.
- There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice. All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper is divided into FIVE sections: Section A, B, C, D and E.
- SECTION A - question number 1 to 18 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- SECTION B question number 19 to 25 are Very Short Answer (VSA) type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION C - question number 26 to 30 are Short Answer (SA) type questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION D question number 31 and 32 are case-based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- SECTION E question number 33 to 35 are Long Answer (LA) questions carrying 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions in Section B, 2 questions in Section C, 2 questions in Section D and 2 questions in section E.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed
Which of the following molecules has a chiral centre correctly labelled with an asterisk (*)?
CH3C*HBrCH3
CH3C*HClCH2Br
HOCH2C*H(OH)CH2OH
CH3C*Br2CH3
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Which of the following alcohols will not undergo oxidation?
Butanol
Butan-2-ol
2-Methylbutan-2-ol
3-Methylbutan-2-ol
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
A voltaic cell is made by connecting two half cells represented by half equations below:
\[\ce{Sn^{2+}_{ (aq)} + 2e^- -> Sn_{(s)}}\], E0 = − 0.14 V
\[\ce{Fe^{3+}_{ (aq)} + e^- -> Fe^{2+}_{ (aq)}}\], E0 = + 0.77 V
Which statement is correct about this voltaic cell?
Fe2+ is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is −0.91 V.
Sn is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.91 V.
Fe2+ is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.91 V.
Sn is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.63 V.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Four half-reactions, I to IV are shown below:
- \[\ce{2Cl^- -> Cl2 + 2e^-}\]
- \[\ce{4OH^- -> O2 + 2H2O + 2e^-}\]
- \[\ce{Na^+ + e^- -> Na}\]
- \[\ce{2H^+ + 2e^- -> H2}\]
Which two of these reactions are most likely to occur when concentrated brine is electrolysed?
I and III
II and III
I and IV
II and IV
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Which property of transition metals enables them to behave as catalysts?
High melting point
High ionisation enthalpy
Alloy formation
Variable oxidation states
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
In the two tetrahedral structures of dichromate ion, ______.
4 Cr–O bonds are equivalent in length
6 Cr–O bonds are equivalent in length
All Cr–O bonds are equivalent in length
All Cr–O bonds are non-equivalent
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
1 mole of liquid A and 2 moles of liquid B make a solution having a total vapour pressure of 40 torr. The vapour pressure of pure A and pure B are 45 torr and 30 torr, respectively. The above solution ______.
is an ideal solution
shows positive deviation
shows negative deviation
is a maximum boiling azeotrope
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Which of the following would not be a good choice for reducing nitrobenzene to aniline?
LiAlH4
H2/Ni
Fe and HCl
Sn and HCl
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
If the molality of a dilute solution is doubled, the value of the molal elevation constant (Kb) will be ______.
halved
tripled
doubled
unchanged
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called ______.
inversion
hydration
esterification
saponification
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Which one of the following has the lowest pKa value?
CH3 – COOH
O2N–CH2–COOH
Cl–CH2–COOH
HCOOH
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Which of the following cell was used in the Apollo space programme?
Mercury cell
Daniel cell
\[\ce{H2 - O2}\] fuel cell
Dry cell
\[\ce{Ni - Cd}\] cell
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
The following experimental rate data were obtained for a reaction carried out at 25°C:
\[\ce{A_{(g)} + B_{(g)} -> C_{(g)} + A_{(g)}}\]
| Initial [A(g)]/mol dm−3 | Initial [B(g)]/mol dm−3 | Initial rate/mol dm−3s−1 |
| 3.0 × 10−2 | 2.0 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−4 |
| 3.0 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−4 |
| 6.0 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−2 | 7.56 × 10−4 |
What are the orders with respect to A(g) and B(g)?
| Order with respect to A(g) | Order with respect to B(g) |
| Zero | Second |
| Order with respect to A(g) | Order with respect to B(g) |
| First | Zero |
| Order with respect to A(g) | Order with respect to B(g) |
| Second | Zero |
| Order with respect to A(g) | Order with respect to B(g) |
| Second | First |
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
The magnetic moment of [NiCl4]2− is ______.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
1.82 BM
2.82 BM
4.42 BM
5.46 BM
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bonds.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Assertion (A): For a zero-order reaction, the unit of rate constant and rate of reaction are same.
Reason (R): Rate of reaction for zero order reaction is independent of concentration of reactant.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Assertion (A): Acetic acid but not formic acid, can be halogenated in the presence of red P and Cl2.
Reason (R): Acetic acid is a weaker acid than formic acid.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Assertion (A): Trans [CrCl2(ox)2]3− shows optical isomerism.
Reason (R): Optical isomerism is common in octahedral complexes involving didentate ligands.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
What should be the signs (positive/negative) for \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] and ΔG0 for a spontaneous redox reaction occurring under standard conditions?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
State Faraday's first law of electrolysis.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Calculate the emf of the following cell at 298 K:
Fe(s) | Fe2+ (0.01 M) | | H+ (1 M) | H2(g) (1 bar) Pt(s)
Given \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] = 0.44 V.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
What happens to the rate constant k and activation energy Ea as the temperature of a chemical reaction is increased? Justify.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Which of the following species cannot act as a ligand? Give reason.
OH−
`"NH"_4^+`
CH3NH2
H2O
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
The complex [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 is red in colour. Give IUPAC the name of its linkage isomer.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Why is the boiling point of o-dichlorobenzene higher than p-dichlorobenzene, but the melting point of para-isomer is higher than ortho-isomer?
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Advertisements
For the pair phenol and cyclohexanol, answer the following:
Why is phenol more acidic than cyclohexanol?
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
For the pair phenol and cyclohexanol, answer the following:
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the two.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Draw the zwitter ion structure for sulphanilic acid.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
How can the activating effect of the −NH2 group in aniline be controlled?
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Complete the reaction with the main product formed:

Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Convert bromoethane to propanamine.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Give the reaction of glucose with hydrogen cyanide. Presence of which group is confirmed by this reaction?
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
For the reaction \[\ce{2N2O5_{(g)} -> 4NO2_{(g)} + O2_{(g)}}\] at 318 K. Calculate the rate of reaction if the rate of disappearance of N2O5(g) is 1.4 × 10−3 ms−1.
Chapter:
Show that the time required for 99% completion is double of the time required for the completion of 90% reaction.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
On the basis of Crystal Field theory, write the electronic configuration for the d5 ion with a strong field ligand for which Δ0 > P.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
[Ni(CO)4] has tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN)4]2− has square planar, yet both exhibit diamagnetism. Explain.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Illustrate Sandmeyer's reaction with an equation.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Explain why (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in aqueous solution.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give a reason for the following observations:
Penta-acetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Give a reason for the following observations:
Amino acids behave like salts.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Give a reason for the following observations:
Water soluble vitamins must be taken regularly in the diet.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Give a reason for the following observations:
The two strands in DNA are complementary to each other.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Why is the C-O bond length in phenols less than that in methanol?
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Advertisements
Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling point:
Ethoxyethane, Butanal, Butanol, n-butane
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
How can phenol be prepared from anisole? Give reaction.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Give the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH ->[H2SO4][413 K] CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 + H2O}\]
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
What is meant by hydroboration-oxidation reaction? Illustrate it with an example.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
|
Nucleophilic Substitution: Influences of solvent polarity: The reaction rate (SN2) of 2-bromopropane and NaOH in ethanol containing 40% water is twice slower than in absolute ethanol. Hence the level of solvent polarity has an influence on both SN1 and SN2 reactions but with different results. Generally speaking, a weak polar solvent is favourable for SN2 reaction, while a strong polar solvent is favourable for SN1. Generally speaking, the substitution reaction of tertiary haloalkane is based on SN1 mechanism in solvents with a strong polarity (for example ethanol containing water). |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why racemisation occurs in SN1? (1)
(b) Why is ethanol less polar than water? (1)
(c) Which one of, the following in each pair is more reactive towards SN2 reaction? (2)
(i) CH3 – CH2 – I or CH3CH2 – Cl
(ii)
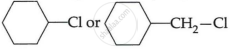
OR
(c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards SN1 reactions: (2)
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-pentane, 2-Bromo-pentane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-3- methylbutane
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| Rahul set up an experiment to find the resistance of aqueous KCl solution for different concentrations at 298 K using a conductivity cell connected to a Wheatstone bridge. He fed the Wheatstone bridge with a.c. power in the audio frequency range 550 to 5000 cycles per second. Once the resistance was calculated from the null point, he also calculated the conductivity K and molar conductivity ∧m and recorded his readings in tabular form. |
| S. No. | Conc. (M) |
k S cm−1 | ∧m S cm2 mol−1 |
| 1. | 1.00 | 111.3 × 10−3 | 111.3 |
| 2. | 0.10 | 12.9 × 10−3 | 129.0 |
| 3. | 0.01 | 1.41 × 10−3 | 141.0 |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why does conductivity decrease with dilution? (1)
(b) If `∧_"m"^0` of KCl is 150.0 S cm2 mol−1, calculate the degree of dissociation of 0.01 M KCI. (1)
(c) If Rahul had used HCl instead of KCl then would you expect the ∧m values to be more or less than those per KCl for a given concentration? Justify. (2)
OR
(c) Amit a classmate of Rahul repeated the same experiment with CH3COOH solution instead of KCl solution. Give one point that would be similar and one that would be different in his observations as compared to Rahul. (2)
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Why is boiling point of 1 M NaCl solution more than that of 1 M glucose solution?
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
A non-volatile solute 'X' (molar mass = 50 g mol−1), when dissolved in 78 g of benzene, reduced its vapour pressure to 90%. Calculate the Mass of X dissolved in the solution.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Calculate the boiling point elevation for a solution prepared by adding 10 g of MgCl2 to 200 g of water, assuming MgCl2 is completely dissociated.
(Kb for Water = 0.512 K kg mol−1, Molar mass MgCl2 = 95 g mol−1)
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Why is the value of van't Hoff factor for ethanoic acid in benzene close to 0.5?
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 2.32 × 10−2 g of K2SO4 in 2L of solution at 25°C assuming that K2SO4 is completely dissociated.
(R = 0.082 L atm K−1 mol, Molar mass K2SO4 = 174 g mol−1)
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
When 25.6 g of sulphur was dissolved in 1000 g of benzene, the freezing point lowered by 0.512 K. Calculate the formula of sulphur (Sr).
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol−1, Atomic mass of sulphur = 32 g mol−1)
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reaction:
Cannizzaro’s reaction
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Why is the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones lower than that of corresponding carboxylic acids?
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
An organic compound 'A' with molecular formula C5H8O2 is reduced to n-pentane with hydrazine followed by heating with NaOH and glycol. 'A' forms a dioxime with hydroxylamine and gives a positive iodoform and Tollen's test. Identify 'A' and give its reaction for iodoform and Tollen's test.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Give a chemical test to distinguish between ethanal acid and ethanoic acid.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Why is the α-hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones are acidic in nature?
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
An organic compound 'A' with the molecular formula C4H8O2 undergoes acid hydrolysis to form two compounds 'B' and 'C'. Oxidation of 'C' with acidified potassium permanganate also produces 'B'. Sodium salt of 'B' on heating with soda lime gives methane.
- Identify 'A', 'B' and 'C'.
- Out of 'B' and 'C', which will have higher boiling point? Give reason.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
How would you account for the following:
The chemistry of actinoids is more complicated as compared to lanthanoids.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Complete the following reaction and justify that it is a disproportionation reaction:
\[\ce{3MnO^{2-}4 + 4H^+ -> \underline{}\underline{}\underline{}\underline{} + \underline{}\underline{}\underline{}\underline{} + 2H2O}\]
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
The given graph shows the trends in melting points of transition metals:

Explain the reason why Cr has the highest melting point and manganese (Mn) has a lower melting point.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
