Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the two tetrahedral structures of dichromate ion, ______.
Options
4 Cr–O bonds are equivalent in length
6 Cr–O bonds are equivalent in length
All Cr–O bonds are equivalent in length
All Cr–O bonds are non-equivalent
Solution
In the two tetrahedral structures of dichromate ion, 6 Cr–O bonds are equivalent in length.
Explanation:
The Dichromate di-anion is made up of two tetrahedral molecules that share oxygen at their common corner. The structure of the chromate ion is tetrahedral. Due to resonance, the six terminal bonds in the dichromate ion have the same bond length. As a result, all six Cr–O bonds are equivalent.
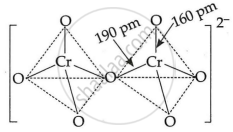
6 Cr–O bonds are equivalent
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give an example and suggest a reason for the following feature of the transition metal chemistry:
The lowest oxide of transition metal is basic, the highest is amphoteric/acidic.
Give an example and suggest a reason for the following feature of the transition metal chemistry:
A transition metal exhibits the highest oxidation state in oxides and fluorides.
Indicate the steps in the preparation of K2Cr2O7 from chromite ore.
Account for the following :
Manganese shows maximum number of oxidation states in 3d series.
\[\ce{KMnO4}\] acts as an oxidising agent in alkaline medium. When alkaline \[\ce{KMnO4}\] is treated with \[\ce{KI}\], iodide ion is oxidised to ______.
In the form of dichromate, \[\ce{Cr (VI)}\] is a strong oxidising agent in acidic medium but \[\ce{Mo (VI)}\] in \[\ce{MoO3}\] \[\ce{and W (VI)}\] in \[\ce{WO3}\] are not because:
(i) \[\ce{Cr(VI)}\] is more stable than \[\ce{Mo(VI)}\] and \[\ce{and W(VI)}\].
(ii) \[\ce{Mo(VI)}\] and \[\ce{and W(VI)}\] are more stable than \[\ce{Cr(VI)}\].
(iii) Higher oxidation states of heavier members of group-6 of transition series are more stable.
(iv) Lower oxidation states of heavier members of group-6 of transition series are more stable.
When \[\ce{Cu^2+}\] ion is treated with \[\ce{KI}\], a white precipitate is formed. Explain the reaction with the help of chemical equation.
Potassium permanganate on heating at 513 K gives a product which is ______.
Complete the reaction mentioning all the products formed:
\[\ce{2KMnO4 ->[\Delta]}\]
Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidified permanganate solution react with oxalic acid? Write the ionic equation for the reaction.
