Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = cos x sin t + cos 2x sin 2t
Solution
The given equation represents a stationary wave because the harmonic terms kxand ωt appear separately in the equation. This equation actually represents the superposition of two stationary waves.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A wire of density ‘ρ’ and Young’s modulus ‘Y’ is stretched between two rigid supports separated by a distance ‘L’ under tension ‘T’. Derive an expression for its frequency in fundamental mode. Hence show that `n=1/(2L)sqrt((Yl)/(rhoL))` where symbols have their usual meanings
A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance take to reach the other end?
A transverse harmonic wave on a string is described by y(x, t) = 3.0 sin (36 t + 0.018 x + π/4)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. The positive direction of x is from left to right.
(a) Is this a travelling wave or a stationary wave?
If it is travelling, what are the speed and direction of its propagation?
(b) What are its amplitude and frequency?
(c) What is the initial phase at the origin?
(d) What is the least distance between two successive crests in the wave?
Explain why (or how) Solids can support both longitudinal and transverse waves, but only longitudinal waves can propagate in gases
A transverse wave is produced on a stretched string 0.9 m long and fixed at its ends. Find the speed of the transverse wave, when the string vibrates while emitting the second overtone of frequency 324 Hz.
Mark out the correct options.
Consider the following statements about sound passing through a gas.
(A) The pressure of the gas at a point oscillates in time.
(B) The position of a small layer of the gas oscillates in time.
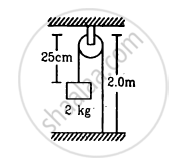
In the arrangement shown in figure , the string has a mass of 4⋅5 g. How much time will it take for a transverse disturbance produced at the floor to reach the pulley? Take g = 10 m s−2.
A wire, fixed at both ends is seen to vibrate at a resonant frequency of 240 Hz and also at 320 Hz. (a) What could be the maximum value of the fundamental frequency? (b) If transverse waves can travel on this string at a speed of 40 m s−1, what is its length?
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
`"y" = 2sqrt(x - "vt")`
