Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How the emf of two cells are compared using potentiometer?
Solution
To compare the emf of two cells, the circuit connections are made as shown in figure. Potentiometer wire CD is connected to a battery Bt and a key K in series. This is the primary circuit. The end C of the wire is connected to the terminal M of a DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw) switch and the other terminal N is connected to a jockey through a galvanometer G and a high resistance HR. The cells whose emf ξ1 and ξ2 to be compared are connected to the terminals M1, N1 and M2, N2 of the DPDT switch.
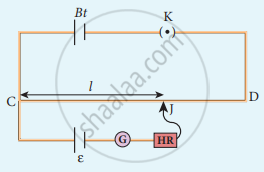
Potentiometer
The positive terminals of Bt, ξ1 and ξ2 should be connected to the same end C. The DPDT switch is pressed towards M1, N1 so that cell ξ1 is included in the secondary circuit and the balancing length l1 is found by adjusting the jockey for zero deflection, Then the second cells ξ2 is included in the circuit and the balancing length l2 is determined. Let r be the resistance per unit length of the potentiometer wire and I be the current flowing through the wire.
we have.
ξ1 = Irl1 …… (1)
ξ2 = Irl2 ……. (2)
By dividing (1) by (2)
`ξ^1/ξ^2 = l^1/l^2` .....(3)
By including a rheostat (Rh) in the primary circuit, the experiment can be repeated several times by changing the current flowing through it.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Kirchhoff's junction law is equivalent to .............................
(a) conservation of energy.
(b) conservation of charge
(c) conservation of electric potential
(d) conservation of electric flux
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in electric networks. How are there rules justified?
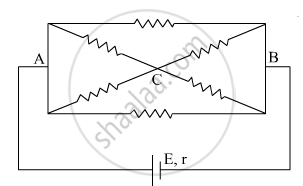
The current is drawn from a cell of emf E and internal resistance r connected to the network of resistors each of resistance r as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for
- the current draw from the cell and
- the power consumed in the network.
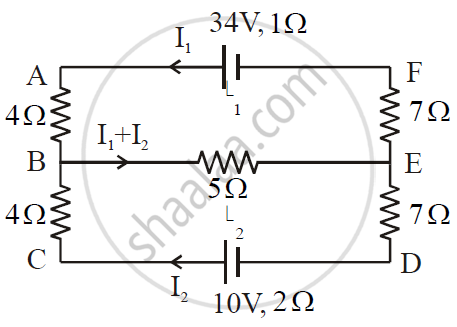
ε1 and ε2 are two batteries having emf of 34V and 10V respectively and internal resistance of 1Ω and 2Ω respectively. They are connected as shown in the figure below. Using Kirchhoff’s Laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I1 and I2.
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
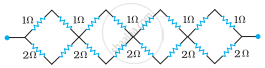
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
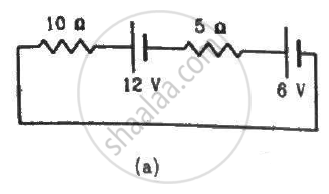
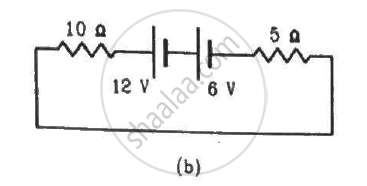
Consider the circuit shown in the figure. Find (a) the current in the circuit (b) the potential drop across the 5 Ω resistor (c) the potential drop across the 10 Ω resistor (d) Answer the parts (a), (b) and (c) with reference to the figure.
State and explain Kirchhoff’s rules.
Kirchhoff s second law is based on the law of conservation of ______
A 6-volt battery is connected to the terminals of a three-metre-long wire of uniform thickness and resistance of 100 ohms. The difference of potential between two points on the wire separated by a distance of 50 cm will be ______.
