Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
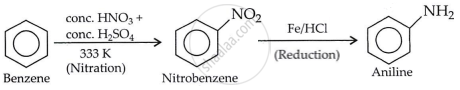
How will you convert Benzene into aniline?
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give reasons for the following: (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength:
C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N, C6H5NH2
Complete the following acid-base reaction and name the product:
\[\ce{(C2H5)3N + HCl ->}\]
Account for the following:
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesising primary amines.
Write a short note on ammonolysis.
Accomplish the following conversion:
Benzene to m-bromophenol
Accomplish the following conversion:
Aniline to p-bromoaniline
Complete the following reactions:
`C_6H_5N_2Cl+H_3PO_2+H_2O->`
Give reasons CH3NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2.
Give reason (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength :
C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, C6H5N(CH3)2
Answer in one sentence.
Arrange the following amines in increasing order of boiling points.
n-propylamine, ethylmethyl amine, trimethylamine.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
Ethyl alcohol, Ethyl amine, Ethanoic acid, Ethane
Which among the following has the highest boiling point?
The CORRECT decreasing order of boiling points is:
A compound Z with molecular formula \[\ce{C3H9N}\] reacts with \[\ce{C6H5SO2Cl}\] to give a solid, insoluble in alkali. Identify Z.
Assertion: N-Ethylbenzene sulphonamide is soluble in alkali.
Reason: Hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulphonamide is strongly acidic.
Which of the following amines form maximum hydrogen bonds within themselves?
Arrange the following in increasing order of their boiling point:
C2H5OH, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)3N
