Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If there were only one type of charge in the universe, then ______.
- `oint_s` E.dS ≠ 0 on any surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS = 0 if the charge is outside the surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS could not be defined.
- `oint_s` E.dS = `q/ε_0` if charges of magnitude q were inside the surface.
Options
a and d
a and c
b and d
c and d
Solution
b and d
Explanation:
From Gauss’ law, we know `oint_s` E.dS = `q/ε_0`, here q is the charge enclosed by the closed surface. If `oint_s` E.dS = 0 then q = 0, i.e., net charge enclosed by the surface must be zero. If the charge is outside the surface, then charge enclosed by the surface is q = 0 and thus, `oint` E.dS = 0.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
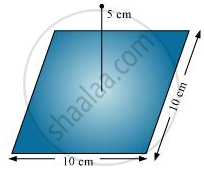
A point charge +10 μC is a distance 5 cm directly above the centre of a square of side 10 cm, as shown in the Figure. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the square? (Hint: Think of the square as one face of a cube with edge 10 cm.)
A thin conducting spherical shell of radius R has charge Q spread uniformly over its surface. Using Gauss’s law, derive an expression for an electric field at a point outside the shell.
Gaussian surface cannot pass through discrete charge because ____________.
The Gaussian surface ______.
Which of the following statements is not true about Gauss’s law?
If `oint_s` E.dS = 0 over a surface, then ______.
- the electric field inside the surface and on it is zero.
- the electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform.
- the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it.
- all charges must necessarily be outside the surface.
Refer to the arrangement of charges in figure and a Gaussian surface of radius R with Q at the centre. Then
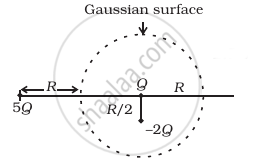
- total flux through the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/ε_0`.
- field on the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/(4 piε_0 R^2)`.
- flux through the surface of sphere due to 5Q is zero.
- field on the surface of sphere due to –2Q is same everywhere.
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the elecric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero.
