Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance
3: Current Electricity
4: Moving Charges And Magnetism
5: Magnetism And Matter
6: Electromagnetic Induction
7: Alternating Current
8: Electromagnetic Waves
9: Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
10: Wave Optics
11: Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
12: Atoms
13: Nuclei
14: Semiconductor Electronics
15: Communication Systems
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Electric Charges And Fields NCERT Exemplar solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Electric Charges And Fields - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Electric Charges And Fields
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Physics [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 1 Electric Charges And Fields MCQ I [Pages 1 - 9]
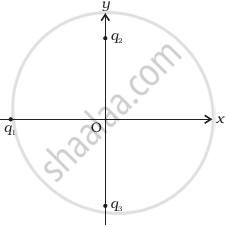
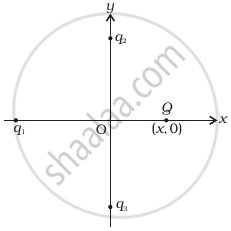
In figure, two positive charges q2 and q3 fixed along the y axis, exert a net electric force in the + x direction on a charge q1 fixed along the x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (x, 0), the force on q1
 (a) |
 (b) |
shall increase along the positive x-axis.
shall decrease along the positive x-axis.
shall point along the negative x-axis.
shall increase but the direction changes because of the intersection of Q with q2 and q3.
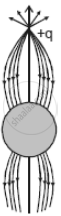
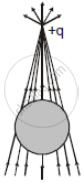
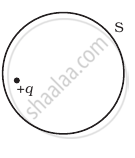
A point positive charge is brought near an isolated conducting sphere (figure). The electric field is best given by ______.
The Electric flux through the surface
 (i) |
 (ii) |
 (iii) |
 (iv) |
in Figure (iv) is the largest.
in Figure (iii) is the least.
in Figure (ii) is same as Figure (iii) but is smaller than Figure (iv)
is the same for all the figures.
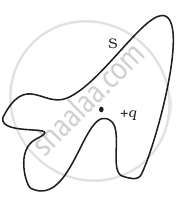
Five charges q1, q2, q3, q4, and q5 are fixed at their positions as shown in figure. S is a Gaussian surface. The Gauss’s law is given by `oint_s E.ds = q/ε_0`
Which of the following statements is correct?
E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from q1, q5 and q3 while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q2 and q4 only.
E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from all charges while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q2 and q4 only.
E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from all charges while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q1, q3 and q5 only.
Both E on the LHS and q on the RHS will have contributions from q2 and q4 only.
Figure shows electric field lines in which an electric dipole P is placed as shown. Which of the following statements is correct?
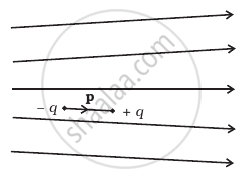
The dipole will not experience any force.
The dipole will experience a force towards right.
The dipole will experience a force towards left.
The dipole will experience a force upwards.
A point charge + q is placed at a distance d from an isolated conducting plane. The field at a point P on the other side of the plane is ______.
directed perpendicular to the plane and away from the plane
directed perpendicular to the plane but towards the plane
directed radially away from the point charge
directed radially towards the point charge
A hemisphere is uniformly charged positively. The electric field at a point on a diameter away from the centre is directed ______.
perpendicular to the diameter
parallel to the diameter
at an angle tilted towards the diameter
at an angle tilted away from the diameter
If `oint_s` E.dS = 0 over a surface, then ______.
- the electric field inside the surface and on it is zero.
- the electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform.
- the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it.
- all charges must necessarily be outside the surface.
a and b
b and c
c and d
a and d
The Electric field at a point is ______.
- always continuous.
- continuous if there is no charge at that point.
- discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point.
- discontinuous if there is a charge at that point.
a and b
b and d
c and d
a and d
If there were only one type of charge in the universe, then ______.
- `oint_s` E.dS ≠ 0 on any surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS = 0 if the charge is outside the surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS could not be defined.
- `oint_s` E.dS = `q/ε_0` if charges of magnitude q were inside the surface.
a and d
a and c
b and d
c and d
Consider a region inside which there are various types of charges but the total charge is zero. At points outside the region
- the electric field is necessarily zero.
- the electric field is due to the dipole moment of the charge distribution only.
- the dominant electric field is `∞ 1/r^3`, for large r, where r is the distance from a origin in this region.
- the work done to move a charged particle along a closed path, away from the region, will be zero.
b and d
a and c
b and d
c and d
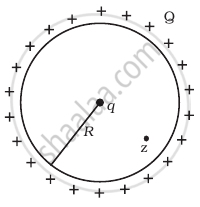
Refer to the arrangement of charges in figure and a Gaussian surface of radius R with Q at the centre. Then
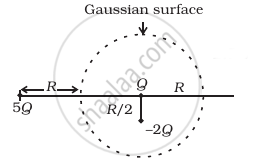
- total flux through the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/ε_0`.
- field on the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/(4 piε_0 R^2)`.
- flux through the surface of sphere due to 5Q is zero.
- field on the surface of sphere due to –2Q is same everywhere.
a and d
a and c
b and d
c and d
A positive charge Q is uniformly distributed along a circular ring of radius R. A small test charge q is placed at the centre of the ring (figure). Then
- If q > 0 and is displaced away from the centre in the plane of the ring, it will be pushed back towards the centre.
- If q < 0 and is displaced away from the centre in the plane of the ring, it will never return to the centre and will continue moving till it hits the ring.
- If q < 0, it will perform SHM for small displacement along the axis.
- q at the centre of the ring is in an unstable equilibrium within the plane of the ring for q > 0.
a and b
b and c
c and d
a, b, c and d
An arbitrary surface encloses a dipole. What is the electric flux through this surface?
A metallic spherical shell has an inner radius R1 and outer radius R2. A charge Q is placed at the centre of the spherical cavity. What will be surface charge density on (i) the inner surface, and (ii) the outer surface?
The dimensions of an atom are of the order of an Angstrom. Thus there must be large electric fields between the protons and electrons. Why, then is the electrostatic field inside a conductor zero?
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the elecric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero.
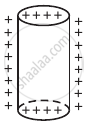
Sketch the electric field lines for a uniformly charged hollow cylinder shown in figure.
What will be the total flux through the faces of the cube (figure) with side of length a if a charge q is placed at

- A: a corner of the cube.
- B: mid-point of an edge of the cube.
- C: centre of a face of the cube.
- D: mid-point of B and C.
A paisa coin is made up of Al-Mg alloy and weighs 0.75g. It has a square shape and its diagonal measures 17 mm. It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charges.
Treating the paisa coins made up of only Al, find the magnitude of equal number of positive and negative charges. What conclusion do you draw from this magnitude?
Consider a coin of Example 1.20. It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charge of magnitude 34.8 kC. Suppose that these equal charges were concentrated in two point charges seperated by (i) 1 cm `(∼ 1/2 xx "diagonal of the one paisa coin")`, (ii) 100 m (~ length of a long 6 building) and (iii) 106 m (radius of the earth). Find the force on each such point charge in each of the three cases. What do you conclude from these results?
Figure represents a crystal unit of cesium chloride, CsCl. The cesium atoms, represented by open circles are situated at the corners of a cube of side 0.40 nm, whereas a Cl atom is situated at the centre of the cube.
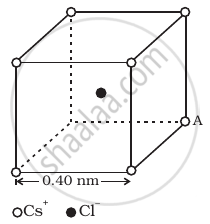
The Cs atoms are deficient in one electron while the Cl atom carries an excess electron.
- What is the net electric field on the Cl atom due to eight Cs atoms?
- Suppose that the Cs atom at the corner A is missing. What is the net force now on the Cl atom due to seven remaining Cs atoms?
Two charges q and – 3q are placed fixed on x-axis separated by distance ‘d’. Where should a third charge 2q be placed such that it will not experience any force?
Figure shows the electric field lines around three point charges A, B and C.

- Which charges are positive?
- Which charge has the largest magnitude? Why?
- In which region or regions of the picture could the electric field be zero? Justify your answer.
(i) near A, (ii) near B, (iii) near C, (iv) nowhere.
Five charges, q each are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side ‘a’ (Figure).
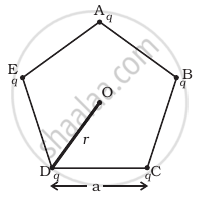
(a) (i) What will be the electric field at O, the centre of the pentagon?
(ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed?
(iii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by –q?
(b) How would your answer to (a) be affected if pentagon is replaced by n-sided regular polygon with charge q at each of its corners?
In 1959 Lyttleton and Bondi suggested that the expansion of the Universe could be explained if matter carried a net charge. Suppose that the Universe is made up of hydrogen atoms with a number density N, which is maintained a constant. Let the charge on the proton be: ep = – (1 + y)e where e is the electronic charge.
- Find the critical value of y such that expansion may start.
- Show that the velocity of expansion is proportional to the distance from the centre.
Consider a sphere of radius R with charge density distributed as
ρ(r) = kr for r ≤ R
= 0 for r > R
- Find the electric field at all points r.
- Suppose the total charge on the sphere is 2e where e is the electron charge. Where can two protons be embedded such that the force on each of them is zero. Assume that the introduction of the proton does not alter the negative charge distribution.
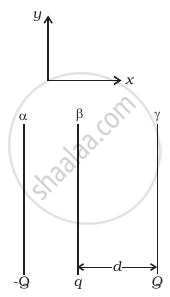
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (α and β), each of surface area S are charged to –Q and q, respectively, where Q > q > 0. A third identical plate (γ), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d (Figure). The third plate is released and collides with the plate β. Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst β and γ.
- Find the electric field acting on the plate γ before collision.
- Find the charges on β and γ after the collision.
- Find the velocity of the plate γ after the collision and at a distance d from the plate β.
There is another useful system of units, besides the SI/mks A system, called the cgs (centimeter-gram-second) system. In this system Coloumb’s law is given by
F = `(Qq)/r^2 hatr`
where the distance r is measured in cm (= 10–2 m), F in dynes (= 10–5 N) and the charges in electrostatic units (es units), where 1 es unit of charge = `1/([3]) xx 10^-9 C`
The number [3] actually arises from the speed of light in vaccum which is now taken to be exactly given by c = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s. An approximate value of c then is c = [3] × 108 m/s.
(i) Show that the coloumb law in cgs units yields
1 esu of charge = 1 (dyne)1/2 cm.
Obtain the dimensions of units of charge in terms of mass M, length L and time T. Show that it is given in terms of fractional powers of M and L.
(ii) Write 1 esu of charge = x C, where x is a dimensionless number. Show that this gives
`1/(4pi ∈_0) = 10^-9/x^2 (N*m^2)/C^2`
With `x = 1/([3]) xx 10^-9`, we have `1/(4pi ∈_0) = [3]^2 xx 10^9 (Nm^2)/C^2`
or, `1/(4pi ∈_0) = (2.99792458)^2 xx 10^9 (Nm^2)/C^2` (exactly).
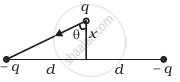
Two charges –q each are fixed separated by distance 2d. A third charge q of mass m placed at the mid-point is displaced slightly by x(x << d) perpendicular to the line joining the two fixed charged as shown in figure. Show that q will perform simple harmonic oscillation of time period.
`T = [(8pi^3 ε_0 md^3)/q^2]^(1/2)`
Total charge –Q is uniformly spread along length of a ring of radius R. A small test charge +q of mass m is kept at the centre of the ring and is given a gentle push along the axis of the ring.
- Show that the particle executes a simple harmonic oscillation.
- Obtain its time period.
Solutions for 1: Electric Charges And Fields
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Electric Charges And Fields NCERT Exemplar solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Electric Charges And Fields - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Electric Charges And Fields
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 12 CBSE 1 (Electric Charges And Fields) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 12 chapter 1 Electric Charges And Fields are Electric Field Due to a System of Charges, Introduction of Electric Field, Continuous Distribution of Charges, Coulomb’s Law - Force Between Two Point Charges, Basic Properties of Electric Charge, Electric Charges, Conductors and Insulators, Superposition Principle - Forces Between Multiple Charges, Physical Significance of Electric Field, Electric Field Lines, Electric Flux, Electric Dipole, Dipole in a Uniform External Field, Gauss’s Law, Applications of Gauss’s Law, Charging by Induction, Electric Field Due to a Point Charge, Uniformly Charged Infinite Plane Sheet and Uniformly Charged Thin Spherical Shell (Field Inside and Outside), Superposition Principle of Forces, Force Between Two Point Charges.
Using NCERT Exemplar Physics [English] Class 12 solutions Electric Charges And Fields exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Physics [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Electric Charges And Fields Physics [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.