Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Refer to the arrangement of charges in figure and a Gaussian surface of radius R with Q at the centre. Then
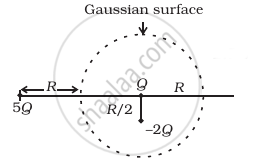
- total flux through the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/ε_0`.
- field on the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/(4 piε_0 R^2)`.
- flux through the surface of sphere due to 5Q is zero.
- field on the surface of sphere due to –2Q is same everywhere.
Options
a and d
a and c
b and d
c and d
Solution
a and c
Explanation:
From Gauss' law, we know `oint_s vecE * dvecS = q_(enclosed)/ε_0`.
Thus, from figure, Total charge inside the Gaussian surface `q_(enclosed)` = Q – 2Q = – Q
The charge 5Q lies outside the surface, thus it makes no contribution to electric flux through the given surface.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
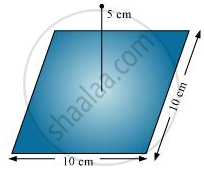
A point charge +10 μC is a distance 5 cm directly above the centre of a square of side 10 cm, as shown in the Figure. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the square? (Hint: Think of the square as one face of a cube with edge 10 cm.)
State Gauss’s law for magnetism. Explain its significance.
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law for magnetism. Explain its significance.
State Gauss's law in electrostatics. Show, with the help of a suitable example along with the figure, that the outward flux due to a point charge 'q'. in vacuum within a closed surface, is independent of its size or shape and is given by `q/ε_0`
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law on electrostatics and drive expression for the electric field due to a long straight thin uniformly charged wire (linear charge density λ) at a point lying at a distance r from the wire.
Gaussian surface cannot pass through discrete charge because ____________.
q1, q2, q3 and q4 are point charges located at points as shown in the figure and S is a spherical gaussian surface of radius R. Which of the following is true according to the Gauss' law?

The Gaussian surface ______.
An arbitrary surface encloses a dipole. What is the electric flux through this surface?
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the elecric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero.
