Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law for magnetism. Explain its significance.
Solution
The net magnetic flux (ΦB) through any closed surface is always zero.
This law suggests that the number of magnetic field lines leaving any closed surface is always equal to the number of magnetic field lines entering it.

Suppose a closed surface S is held in a uniform magnetic field `vecB`.
Consider a small vector area element Δ`vec"S"` of this surface.
Magnetic flux through this area element is defined as ΔΦB = `vec"B".Δvec"S" `
Considering all small area elements of the surface, we obtain net magnetic flux through the surface as:
ØB = `sum_"All" ΔØ_"B" = sum_"All" vec"B". Δvec"S" = 0`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State and explain Gauss’s law.
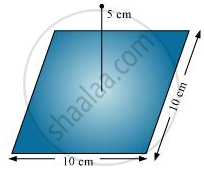
A point charge +10 μC is a distance 5 cm directly above the centre of a square of side 10 cm, as shown in the Figure. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the square? (Hint: Think of the square as one face of a cube with edge 10 cm.)
A charge ‘q’ is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. What is the electric flux passing through each face of the cube?
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law on electrostatics and drive expression for the electric field due to a long straight thin uniformly charged wire (linear charge density λ) at a point lying at a distance r from the wire.
q1, q2, q3 and q4 are point charges located at points as shown in the figure and S is a spherical gaussian surface of radius R. Which of the following is true according to the Gauss' law?

The Electric flux through the surface
 (i) |
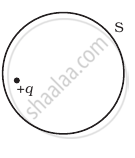 (ii) |
 (iii) |
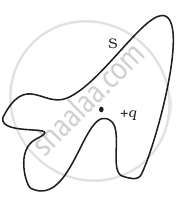 (iv) |
If `oint_s` E.dS = 0 over a surface, then ______.
- the electric field inside the surface and on it is zero.
- the electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform.
- the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it.
- all charges must necessarily be outside the surface.
An arbitrary surface encloses a dipole. What is the electric flux through this surface?
In finding the electric field using Gauss law the formula `|vec"E"| = "q"_"enc"/(epsilon_0|"A"|)` is applicable. In the formula ε0 is permittivity of free space, A is the area of Gaussian surface and qenc is charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface. This equation can be used in which of the following situation?
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. The electric flux through one of its faces is ______.
