Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The dimensions of an atom are of the order of an Angstrom. Thus there must be large electric fields between the protons and electrons. Why, then is the electrostatic field inside a conductor zero?
Solution
The electric fields bind the atoms to neutral entity. Fields are caused by excess charges. There can be no excess charge on the inter surface of an isolated conductor.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, charges appear on both. A similar phenomenon is observed with many other pairs of bodies. Explain how this observation is consistent with the law of conservation of charge.
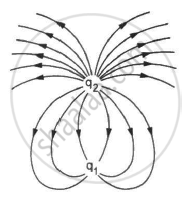
Consider the situation shown in the figure. What are the signs of q1 and q2? If the lines are drawn in proportion to the charges, what is the ratio q1/q2?
In Figure 1 below, a charge Q is fixed. Another charge q is moved along a circular arc MN of radius r around it, from the point M to the point N such that the length of the arc MN = l. The work done in this process is:
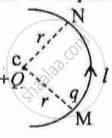
figure 1
Choose the correct option.
Two charges of 1.0 C each are placed one meter apart in free space. The force between them will be
A metallic sphere A isolated from ground is charged to +50 μC. This sphere is brought in contact with other isolated metallics sphere B of half the radius of sphere A. The charge on the two-sphere will be now in the ratio
+2 C and +6 C two charges are repelling each other with a force of 12 N. If each charge is given -2 C of charge, then the value of the force will be ______
The number of lines of force that radiate outwards from one coulomb of charge is:-
Figure represents a crystal unit of cesium chloride, CsCl. The cesium atoms, represented by open circles are situated at the corners of a cube of side 0.40 nm, whereas a Cl atom is situated at the centre of the cube.
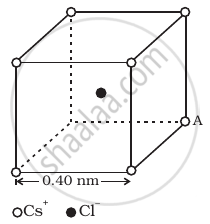
The Cs atoms are deficient in one electron while the Cl atom carries an excess electron.
- What is the net electric field on the Cl atom due to eight Cs atoms?
- Suppose that the Cs atom at the corner A is missing. What is the net force now on the Cl atom due to seven remaining Cs atoms?
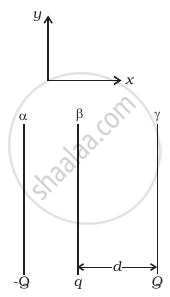
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (α and β), each of surface area S are charged to –Q and q, respectively, where Q > q > 0. A third identical plate (γ), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d (Figure). The third plate is released and collides with the plate β. Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst β and γ.
- Find the electric field acting on the plate γ before collision.
- Find the charges on β and γ after the collision.
- Find the velocity of the plate γ after the collision and at a distance d from the plate β.