Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In Regnault's apparatus for measuring specific heat capacity of a solid, there is an inlet and an outlet in the steam chamber. The inlet is near the top and the outlet is near the bottom. Why is it better than the opposite choice where the inlet is near the bottom and the outlet is near the top?
Solution
The inlet is near the top and the outlet is near the bottom because there is a loss of heat from the steam as it passes through the chamber. As the steam loses heat, a part of it condenses back to water and the cold steam gets denser and moves down towards the bottom.
But when done the other way round, the used steam does not pass through the chamber correctly and gets mixed up. This can result in discrepancy in the desired results.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A child running a temperature of 101°F is given an antipyrin (i.e. a medicine that lowers fever) which causes an increase in the rate of evaporation of sweat from his body. If the fever is brought down to 98 °F in 20 min, what is the average rate of extra evaporation caused, by the drug? Assume the evaporation mechanism to be the only way by which heat is lost. The mass of the child is 30 kg. The specific heat of human body is approximately the same as that of water, and latent heat of evaporation of water at that temperature is about 580 cal g–1.
Calculate the mass of ice needed to cool 150 g of water contained in a calorimeter of mass 50 g at 32 °C such that the final temperature is 5 °C. Specific heat capacity of calorimeter = 0.4 J g-1 °C-1, Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1°C-1, latent heat capacity of ice = 330 J g-1.
Why do the farmers fill their fields with water on a cold winter night?
A mass m1 of a substance of specific heat capacity c1 at temperature t1 is mixed with a mass m2 of other substance of specific heat capacity c2 at a lower temperature t2. Deduce the expression for the temperature t of the mixture. State the assumption made, if any.
The S.I. unit of specific heat capacity is ______.
How much heat energy is released when 5.0 g of water at 20℃ changes into ice at 0℃? Take specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 K-1, Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1.
Name the radiations for which the green house gases are transparent ?
How will rise in sea level affect population in coastal countries?
State three ways to minimize the global warming.
Without green house effect, the average temperature of earth’s surface would have been:
(a) – 18℃
(b) 33℃
(c) 0℃
(d) 15℃
Which principle is used to measure the specific heat capacity of a substance?
A calorimeter has mass 100 g and specific heat 0.1 kcal/ kg °C. It contains 250 gm of liquid at 30°C having specific heat of 0.4 kcal/kg °C. If we drop a piece of ice of mass 10 g at 0°C, What will be the temperature of the mixture?
The substances like water which have ........... Heat capacity warm up more slowly than substances like iron which have .......... heat capacity.
State, with reason, which of the two, boiling water or steam both at 100°C will produce more severe burns.
Explain, why is water sprayed on roads in evening in hot summer?
Explain, why temperature in hot summer, falls sharply after a sharp shower?
An equal quantity of heat is supplied to two substances A and B. The substance A shows a greater rise in temperature. What can you say about the heat capacity of A as compared to that of B?
Is it possible to condense the water formed, back to ice by adding ice at 0°C. Explain with reason.
Some heat is provided to a body to raise its temperature by 25°C. What will be the corresponding rise in temperature of the body as shown on the Kelvin scale?
1 kg of water freezes to form ice at 0°C. What amount of heat is withdrawn?
Why are athletes advised to put on extra clothes after competing on event?
Answer the following question.
Why do we generally consider two specific heats of a gas?
_______ is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C.
The heat capacity of the vessel of mass 100 kg is 8000 J/°K. Find its specific heat capacity.
Numerical Problem.
What is the heat in joules required to raise the temperature of 25 grams of water from 0°C to 100°C? What is the heat in Calories? (Specific heat of water = `(4.18"J")/("g"°"C")`
A monoatomic gas of pressure 'P' having volume 'V' expands isothermally to a volume '2V' and then adiabatically to a volume '16V'. The final pressure of the gas is ______.
(ratio of specific heats = `5/3`)
Heat is applied to a rigid diatomic gas at constant pressure. The ratio ΔQ : ΔU : ΔW is ______.
For a gas `"R"/"C"_"v" = 0.4,` where 'R' is the universal gas constant and 'Cv' is molar specific heat at constant volume. The gas is made up of molecules which are ______.
An office room contains about 4000 moles of air. The change in the internal energy of this much air when it is cooled from 34° C to 19° C at a constant pressure of 1.0 atm is (Use `gamma_"air"` = 1.4 and Universal gas constant = 8.314 J / mol K) ____________.
The molar specific heat of an ideal gas at constant pressure and constant volume is 'Cp' and 'Cv' respectively. If 'R' is the universal gas constant and the ratio 'Cp' to 'Cv' is 'γ' then CV = ______.
The ratio of the specific heats `c_"p"/c_"v"=gamma` in terms of degrees of freedom 'n' is given by ______.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for 200 g of water. The heat is extracted at the rate of 100 Js-1. Answer the questions that follow:
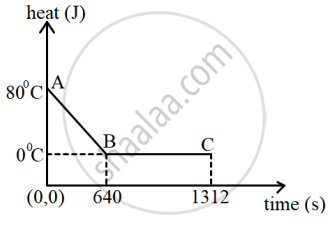
- Calculate specific heat capacity of water.
- Heat released in the region BC.
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B | ||
| 1. | Specific heat capacity of water | a. | 0°C |
| 2. | Latent heat of fusion of ice | b. | 2260 J/g |
| 3. | Latent heat of vaporization of water | c. | 100°C |
| 4. | The melting point of iced | d. | 4.2 J/g°C |
| 5. | The boiling point of water | e. | 336 J/g |
A metal ball of heat capacity 50J/°C loses 2000 J of heat. By how much will its temperature fall?
Two blocks P and Q of different metals having their mass in the ratio 2 : 1 are given same amount of heat. Their temperature rises by same amount. Compare their specific heat capacities.
Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as heat reservoir.
