Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Why do we generally consider two specific heats of a gas?
Solution
- A slight change in temperature causes a considerable change in pressure as well as the volume of the gas.
- Therefore, two principal specific heats are defined for a gas viz., specific heat capacity at constant volume (SV), and specific heat capacity at constant pressure (SP).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A child running a temperature of 101°F is given an antipyrin (i.e. a medicine that lowers fever) which causes an increase in the rate of evaporation of sweat from his body. If the fever is brought down to 98 °F in 20 min, what is the average rate of extra evaporation caused, by the drug? Assume the evaporation mechanism to be the only way by which heat is lost. The mass of the child is 30 kg. The specific heat of human body is approximately the same as that of water, and latent heat of evaporation of water at that temperature is about 580 cal g–1.
Define heat capacity and state its SI unit.
Calculate the mass of ice required to lower the temperature of 300 g of water 40°C to water at 0°C.
(Specific latent heat of ice = 336 J/g, the Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2J/g°C)
What do you understand by the following statements:
The heat capacity of the body is 60JK-1.
Water in lakes and ponds do not freeze at once in cold countries. Give a reason is support of your answer.
During the phase change does the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance increase?
Write the approximate value of specific heat capacity of water in S.I. unit.
Why do the farmers fill their fields with water on a cold winter night?
Discuss the role of high specific heat capacity of water with reference to climate in coastal areas.
Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as cooling purposes?
The S.I. unit of specific heat capacity is ______.
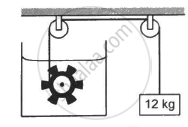
Figure shows a paddle wheel coupled to a mass of 12 kg through fixed frictionless pulleys. The paddle is immersed in a liquid of heat capacity 4200 J K−1 kept in an adiabatic container. Consider a time interval in which the 12 kg block falls slowly through 70 cm. (a) How much heat is given to the liquid? (b) How much work is done on the liquid? (c) Calculate the rise in the temperature of the liquid neglecting the heat capacity of the container and the paddle.
A liquid X has specific heat capacity higher than the liquid Y. Which liquid is useful as heat reservoir to keep juice bottles without freezing?
Water boils at 120 °C in a pressure cooker. Explain the reason
Explain, why does a wise farmer water his fields, if forecast is forst?
If substances A and B are liquids then which one would be more useful in car radiators?
Given: Specific heat capacity’A’ 3.8 J/g /K. Specific heat capacity ‘B’ 0.4 J/g /K.
An equal quantity of heat is supplied to two substances A and B. The substance A shows a greater rise in temperature. What can you say about the heat capacity of A as compared to that of B?
A piece of iron of mass 2.0 kg has a thermal capacity of 966 J/°C. What is its specific heat capacity in S.I. units?
Calculate the ratio of two specific heats of polyatomic gas molecules.
Read this activity and answer the following questions.
- Take three spheres of iron, copper and lead. the lead of equal mass.
- Put all the three spheres in boiling water in the beaker for some time.
- Take the three spheres out of the water.
- All the spheres will be at a temperature 100 °C.
- Put them immediately on the thick slab of wax.
- Note, the depth that each of the sphere goes into the wax.
Questions:
- Which property is determined from this activity?
- Give name to that property.
- Explain the term principal of heat exchange with the help of this activity.
For a gas, `"R"/"C"_"v"=0.4`, where R Is universal gas constant and Cv is the molar specific heat at constant volume. The gas is made up of molecules, which are ______
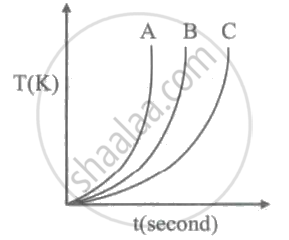
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific beat?
Two metals A and B have specific heat capacities in the ratio 2:3. If they are supplied same amount of heat then
If specific heat capacity of metal A is 0.26 Jg-1 0C-1 then calculate the specific heat capacity of metal B.
Match the following
| 1. | Specific heat capacity | a. | Dewar bottle |
| 2. | Calorimeter | b. | Lavoisier and Simon |
| 3. | Vacuum flask | c. | J Kg-1 K-1 |
| 4. | Ice – calorimeter | d. | Heat capacity |
Find the odd one out:
Specific heat capacity of a substance X is 1900 Jkg-1°C-1 means ______.
Prove the Mayer's relation `C_p - C _v = R/J`
