Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given figure, AB || EC, AB = AC and AE bisects ∠DAC. Prove that:
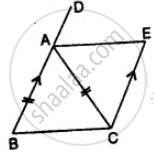
- ∠EAC = ∠ACB
- ABCE is a parallelogram.
Solution
ABCE is a quadrilateral in which AC is its diagonal and AB || EC, AB = AC
BA is produced to D
AE bisects ∠DAC
To prove:
(i) ∠EAC = ∠ACB
(ii) ABCE is a parallelogram
Proof:
(i) In ∆ABC and ∆AEC
AC = AC (common)
AB || CE (given)
∠BAC = ∠ACE (Alternate angle)
∆ABC = ∆AEC (SAS Axiom)
(ii) ∠BCA = ∠CAE (c.p.c.t.)
But these are alternate angles
AE || BC
But AB || EC (given)
∴ ABCE is a parallelogram
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can a quadrilateral ABCD be a parallelogram if AB = DC = 8 cm, AD = 4 cm and BC = 4.4 cm?
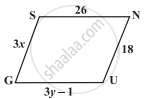
The following figure GUNS is a parallelogram. Find x and y. (Lengths are in cm)
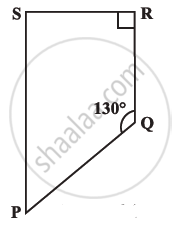
Find the measure of ∠P and ∠S, if `bar(SP) || bar(RQ)` in the following figure. (If you find m∠R, is there more than one method to find m∠P?).
Perimeter of a parallelogram is 150 cm. One of its sides is greater than the other side by 25 cm. Find the lengths of all sides.
Ratio of two adjacent sides of a parallelogram is 3 : 4, and its perimeter is 112 cm. Find the length of its each side.
Construct a parallelogram ABCD such that l(BC) = 7 cm, m∠ABC = 40° , l(AB) = 3 cm.
ABCD is a parallelogram. What kind of quadrilateral is it if: AC is perpendicular to BD but is not equal to it?
The angle between the two altitudes of a parallelogram through the same vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 30°. The measure of the obtuse angle is ______.
Two angles of a quadrilateral are each of measure 75° and the other two angles are equal. What is the measure of these two angles? Name the possible figures so formed.
Draw a rough figure of a quadrilateral that is not a parallelogram but has exactly two opposite angles of equal measure.
