Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | SN1 reaction | (a) vic-dibromides |
| (ii) | Chemicals in fire extinguisher | (b) gem-dihalides |
| (iii) | Bromination of alkenes | (c) Racemisation |
| (iv) | Alkylidene halides | (d) Saytzeff rule |
| (v) | Elimination of HX from alkylhalide | (e) Chlorobromocarbons |
Solution
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | SN1 reaction | (c) Racemisation |
| (ii) | Chemicals in fire extinguisher | (e) Chlorobromocarbons |
| (iii) | Bromination of alkenes | (a) vic-dibromides |
| (iv) | Alkylidene halides | (b) gem-dihalides |
| (v) | Elimination of HX from alkylhalide | (d) Saytzeff rule |
Explanation:
(i) A mixture containing two enantiomers in equal proportions will have zero optical rotation, such a mixture is known as racemic mixture. The process of conversion of enantiomer into a racemic mixture is known as racemisation. If an alkyl halide follows SN1 mechanism then racemisation takes place while if it follows SN2 mechanism than inversion takes places.
(ii) Chlorobromocarbons are used in fire extinguishers.
(iii) In vicinal dihalides, halogen atoms are present on the adjacent carbon atom. Bromination of alkanes will give vicinal dihalides.
(iv) Alkylidene halides are named gem-dihalides. In gem-dihalides halogen atoms are present on same carbon atom.
(v) Elimination of HX from alkylhalide follows Saytzeff rule. This rule states that “in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the preferred product is that alkene which has the greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms”.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2I
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3CH=CHC(Br)(CH3)2
Identify the compound Y in the following reaction.
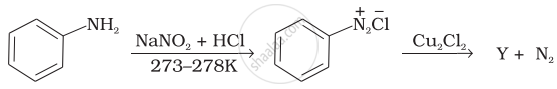
The reaction of toluene with chlorine in the presence of iron and in the absence of light yields ______.
Haloalkanes contain halogen atom (s) attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of an alkyl group. Identify haloalkane from the following compounds.
(i) 2-Bromopentane
(ii) Vinyl chloride (chloroethene)
(iii) 2-chloroacetophenone
(iv) Trichloromethane
Which alkyl halide has maximum density
Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
\[\ce{CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2I}\]
Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
CH3C(Cl)(C2H5 )CH2CH3
Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
\[\ce{CH3C(C2H5)2CH2Br}\]
Name the following halide according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
\[\ce{CH3C(C2H5)2CH2Br}\]
