Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the following data:
| Government School, Chandpur | ||
| Daily Attendance | Date: 15.4.2009 | |
| Class | Total Students | Number of Students Present on that Day |
| VI | 90 | 81 |
| VII | 82 | 76 |
| VIII | 95 | 91 |
| IX | 70 | 65 |
| X | 63 | 62 |
- Draw a double bar graph choosing an appropriate scale. What do you infer from the bar graph?
- Which class has the maximum number of students?
- In which class, the difference of total students and number of students present is minimum?
- Find the ratio of number of students present to the total number of students of Class IX.
- What per cent of Class VI students were absent?
Solution
a. A double bar graph is shown below:

We infer from the bar graph that maximum number of students were absent in class VI on 15.04.2009, whereas minimum number of students were absent in class X.
b. Clearly, class VIII has maximum number of students, i.e. 95.
c. The difference of total number of students and number of students present is minimum for class X i.e. 63 – 62 = 1.
d. Number of students present in class IX = 65
Total number of students in class IX = 70
Hence, required ratio = `65/70 = 13/14` or 13:14
e. Total number of students in class VI = 90
Number of students present in class VI = 81
Number of absent students = 90 – 81 = 9
∴ Percentage of absent students of class VI = `("Number of absent students"/"Total number of students" xx 100)%`
= `(9/90 xx 100)%`
= 10%
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Number of children in six different classes are given below. Represent the data on a bar graph.
| Class | Fifth | Sixth | Seventh | Eighth | Ninth | Tenth |
| Number of children | 135 | 120 | 95 | 100 | 90 | 80 |
- How would you choose a scale?
- Answer the following questions:
- Which class has the maximum number of children? And the minimum?
- Find the ratio of students of class sixth to the students of class eight.
Comparison of parts of a whole may be done by a ______.
The following chart gives the growth in height in terms of percentage of full height of boys and girls with their respective ages.
| Age (in years) | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
18 |
| Boys | 72% | 75% | 78% | 81% | 84% | 88% | 92% | 95% | 98% | 99% | 100% |
| Girls | 77% | 81% | 84% | 88% | 91% | 95% | 98% | 99% | 99.5% | 100% | 100% |
Draw the line graph of above data on the same sheet and answer the following questions.
- In which year both the boys and the girls achieve their maximum height?
- Who grows faster at puberty (14 years to 16 years of age)?
The following bar graph represents the data for different sizes of shoes worn by the students in a school. Read the graph and answer the following questions.
Scale: 1 unit length = 50 students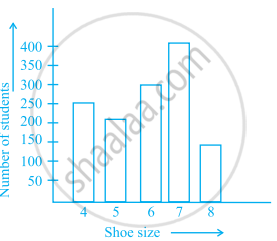
(a) Find the number of students whose shoe sizes have been collected.
(b) What is the number of students wearing shoe size 6?
(c) What are the different sizes of the shoes worn by the students?
(d) Which shoe size is worn by the maximum number of students?
(e) Which shoe size is worn by minimum number of students?
(f) State whether true or false:
The total number of students wearing shoe sizes 5 and 8 is the same as the number of students wearing shoe size 6.
The following graph gives the information about the number of railway tickets sold for different cities on a railway ticket counter between 6.00 am to 10.00 am. Read the bar graph and answer the following questions.
Scale: 1 unit length = 10 tickets
(a) How many tickets were sold in all?
(b) For which city were the maximum number of tickets sold?
(c) For which city were the minimum number of tickets sold?
(d) Name the cities for which the number of tickets sold is more than 20
(e) Fill in the blanks: Number of tickets sold for Delhi and Jaipur together exceeds the total number of tickets sold for Patna and Chennai by ______.
Prepare a bar graph of the data given in
| Surname | Number of people |
| Khan |  |
| Patel |  |
| Rao |  |
| Roy |  |
| Saikia |  |
| Singh |  |
The representation of data with bars of uniform width is called ______.
Observe the given bar graph carefully and answer the questions that follow.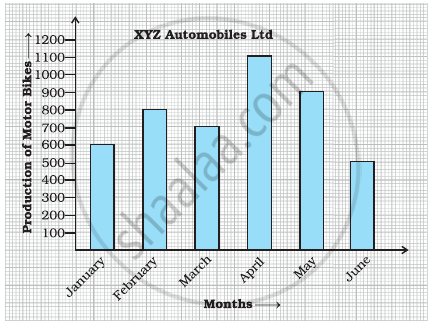
- What information does the bar graph depict?
- How many motor bikes were produced in the first three months?
- Calculate the increase in production in May over the production in January.
- In which month the production was minimum and what was it?
- Calculate the average (mean) production of bikes in 6 months.
Study the bar graph given below and answer the questions that follow:

- What information is depicted from the bar graph?
- In which subject is the student very good?
- Calculate the average marks of the student.
- If 75 and above marks denote a distinction, then name the subjects in which the student got distinction.
- Calculate the percentage of marks the student got out of 500.
Observe the given data:
| Days of the week |
Mon | Tues | Wed | Thurs | Fri | Sat |
| Number of Mobile Phone Sets Sold |
50 | 45 | 30 | 55 | 27 | 60 |
- Draw a bar graph to represent the above given information.
- On which day of the week was the sales maximum?
- Find the total sales during the week.
- Find the ratio of the minimum sale to the maximum sale.
- Calculate the average sale during the week.
- On how many days of the week was the sale above the average sales?
