Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Obtain an expression for average power of AC over a cycle. Discuss its special cases.
Solution
It is given by the product of the voltage and current. In an AC circuit, the voltage and current vary continuously with time. Let us first calculate the power at an instant and then it is averaged over a complete cycle.
The alternating voltage and alternating current in the series RLC circuit at an instant are given by
υ = Vm sin ωt and i = Im sin (ωt + 4>)
where φ is the phase angle between υ and i. The instantaneous power is then written as
P = υi = Vm Im sin ωt sin(ωt + φ)
= Vm Im sin ωt (sin ωt cos φ – cos ωt sin φ)
P = Vm Im (cos φ sin2 ωt – sin ωt cos ωt sin φ) …… (1)
Here the average of sin2 ωt over a cycle is `1/2` and that of sin ωt cos ωt is zero. Substituting these values, we obtain average power over a cycle.
Pav = Vm Im cos φ `xx 1/2 = "V"_"m"/sqrt2 "I"_"m"/sqrt2` cos φ
Pav = VRMS IRMS cos φ …… (2)
where VRMS IRMS is called apparent power and cos φ is power factor. The average power of an AC circuit is also known as the true power of the circuit.
Special Cases:
- For a purely resistive circuit, the phase angle between voltage and current is zero and cos
φ = 1.
∴ Pav = VRMS IRMS - For a purely inductive or capacitive circuit, the phase angle is
`+- pi/2 and cos (+- pi/2) = 0`
∴ Pav = 0 - For series RLC circuit, the phase angle φ = tan-1 `(("x"_"L" - "x"_"c")/"R")`
∴ Pav = VRMS IRMS cos φ
-
For series RLC circuit at resonance, the phase angle is zero and cos φ = 1.
∴ Pav = VRMS IRMS
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why is choke coil needed in the use of fluorescent tubes with ac mains?
The phase relationship between current and voltage in a pure resistive circuit is best represented by ______.
An alternating voltage source of variable angular frequency ‘w’ and fixed amplitude ‘V’ is connected in series with a capacitance C and electric bulb of resistance R(inductance zero). When ‘w’ is increased ______.
In an a.c circuit, peak value of voltage is 423 volts, its effective voltage is ______.
Which of the following is independent of the frequency of a.c?
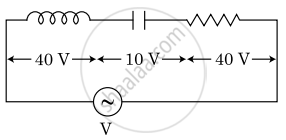
An inductor of inductance L, a capacitor of capacitance C and a resistor of resistance ‘R’ are connected in series to an ac source of potential difference ‘V’ volts as shown in figure. Potential difference across L, C and R is 40 V, 10 V and 40 V, respectively. The amplitude of current flowing through LCR series circuit is `10sqrt2` A. The impedance of the circuit is :
For a series LCR circuit, I vs ω curve is shown:
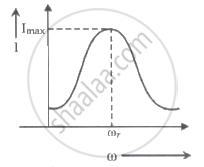
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly capacitive.
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly inductive.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is equal to the resistance of the circuit.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is 0.
An inductor coil stores 64 J of magnetic field energy and dissipates energy at the rate of 640 W when a current of 8 A is passed through it. If this coil is joined across an ideal battery, find the time constant of the circuit in seconds ______.
A 50 Hz AC source of 20 volts is connected across R and C as shown in figure. The voltage across R is 12 volt. The voltage across c is ______.
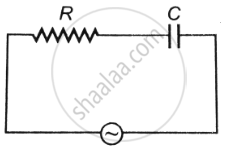
A series CR circuit with R = 200 Ω and C = (50/π) µF is connected across an ac source of peak voltage ε0 = 100 V and frequency v = 50 Hz. Calculate (a) impedance of the circuit (Z), (b) phase angle (Φ), and (c) voltage across the resistor.
