Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend?
List the factors on which the resistance of a uniform cylindrical conductor of a given material depends.
List two factors on which the resistance of a rectangular conductor depends.
Solution
Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends:
- Length of conductor: Resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor. This means Resistance increases with an increase in the length of the conductor. This is the cause that long electric wires create more resistance to the electric current.
- Area of cross-section: Resistance is inversely proportional to the area of the cross-section of the conductor. This means Resistance will decrease with an increase in the area of the conductor and vice versa. This is the cause that thick copper wire creates less resistance to the electric current.
- Temperature: Resistance is directly proportional to the temperature.
- Nature of material: Some materials create the least hindrance and hence are called good conductors. Silver is the best conductor of electricity. While some other materials create more hindrance in the flow of electric current, i.e. flow of electrons through them. Such materials are called bad conductors. Bad conductors are also known as insulators. The hard plastic is one of the best insulators of electricity.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use the data in the Table given below to answer the following –
Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor?
Table give below Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C
| Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C | ||
| − | Material | Resistivity (Ω m) |
| Conductors |
Silver | 1.60 × 10−8 |
| Copper | 1.62 × 10−8 | |
| Aluminium | 2.63 × 10−8 | |
| Tungsten | 5.20 × 10−8 | |
| Nickel | 6.84 × 10−8 | |
| Iron | 10.0 × 10−8 | |
| Chromium | 12.9 × 10−8 | |
| Mercury | 94.0 × 10−8 | |
| Manganese | 1.84 × 10−6 | |
| Alloys |
Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) |
49 × 10−6 |
| Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) |
44 × 10−6 | |
| Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) |
100 × 10−6 | |
| Insulators | Glass | 1010 − 1014 |
| Hard rubber | 1013 − 1016 | |
| Ebonite | 1015 − 1017 | |
| Diamond | 1012 − 1013 | |
| Paper (dry) | 1012 | |
What is (a) the highest, (b) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?
Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be:
A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 × 10−8Ω m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 Ω? How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled?
Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission?
List the factors on which the resistance of a conductor in the shape of a wire depends.
What is meant by conductors and insulators? Give two examples of conductors and two of insulators.
What is the general name of the substances having infinitely high electrical resistance?
Classify the following into good conductors, resistors and insulators:
Rubber, Mercury, Nichrome, Polythene, Aluminium, Wood, Manganin, Bakelite, Iron, Paper, Thermocol, Metal coin
What happens to the resistance as the conductor is made thinner?
What happens to the resistance as the conductor is made thicker?
Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor of electricity?
Which has more resistance:
a long piece of nichrome wire or a short one?
What do you understand by the "resistivity" of a substance?
What would be the effect on the resistance of a metal wire of:
increasing its length?
How does the resistance of a wire change when:
its material is changed to one whose resistivity is three times?
The figure blow shows a variable resistor in a dimmer switch.
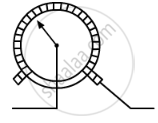
How would you turn the switch to make the lights: (a) brighter, and (b) dimmer? Explain your answer.
Resistance of a metal wire of length 5 m is 100 Ω . If the area of cross - section of the wire is `3 × 10^-7 "m"^2` , Calculate the resistivity of the metal .
The element used almost exclusively for filaments of incandescent lamps:
Assertion: Conductors allow the current to flow through themselves.
Reason: They have free charge carriers.
Use the data in the Table given below to answer the following –
Which material is the best conductor?
Table give below Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C
| Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C | ||
| − | Material | Resistivity (Ω m) |
| Conductors |
Silver | 1.60 × 10−8 |
| Copper | 1.62 × 10−8 | |
| Aluminium | 2.63 × 10−8 | |
| Tungsten | 5.20 × 10−8 | |
| Nickel | 6.84 × 10−8 | |
| Iron | 10.0 × 10−8 | |
| Chromium | 12.9 × 10−8 | |
| Mercury | 94.0 × 10−8 | |
| Manganese | 1.84 × 10−6 | |
| Alloys |
Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) |
49 × 10−6 |
| Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) |
44 × 10−6 | |
| Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) |
100 × 10−6 | |
| Insulators | Glass | 1010 − 1014 |
| Hard rubber | 1013 − 1016 | |
| Ebonite | 1015 − 1017 | |
| Diamond | 1012 − 1013 | |
| Paper (dry) | 1012 | |
How will you infer with the help of an experiment that the same current flows through every part of the circuit containing three resistances in series connected to a battery?
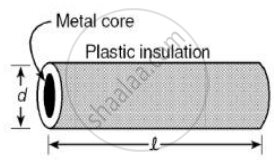
Plastic insulation surrounds a wire having diameter d and length l as shown above. A decrease in the resistance of the wire would be produced by an increase in the ______.
The resistance of a wire of 0.01 cm radius is 10 Ω. If the resistivity of the wire is 50 × 10-8 Ω, find the length of this wire.
How will the resistance of a wire be affected if its
- length is doubled, and
- radius is also doubled ?
Give justification for your answer.
