Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A person goes to bed at sharp 10.00 pm every day. Is it an example of periodic motion? If yes, what is the time period? If no, why?
Solution
No. As motion is a change in position of an object with respect to time or a reference point, it is not an example of periodic motion.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A seconds pendulum is suspended in an elevator moving with constant speed in downward direction. The periodic time (T) of that pendulum is _______.
A copper metal cube has each side of length 1 m. The bottom edge of the cube is fixed and tangential force 4.2x108 N is applied to a top surface. Calculate the lateral displacement of the top surface if modulus of rigidity of copper is 14x1010 N/m2.
Answer in brief:
Derive an expression for the period of motion of a simple pendulum. On which factors does it depend?
The length of the second’s pendulum in a clock is increased to 4 times its initial length. Calculate the number of oscillations completed by the new pendulum in one minute.
A particle executes simple harmonic motion with a frequency v. The frequency with which the kinetic energy oscillates is
A particle is fastened at the end of a string and is whirled in a vertical circle with the other end of the string being fixed. The motion of the particle is
Consider a simple harmonic motion of time period T. Calculate the time taken for the displacement to change value from half the amplitude to the amplitude.
The string the spring and the pulley shown in figure are light. Find the time period of the mass m.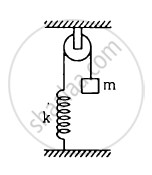
The period of oscillation of a body of mass m1 suspended from a light spring is T. When a body of mass m2 is tied to the first body and the system is made to oscillate, the period is 2T. Compare the masses m1 and m2
A 20 cm wide thin circular disc of mass 200 g is suspended to rigid support from a thin metallic string. By holding the rim of the disc, the string is twisted through 60° and released. It now performs angular oscillations of period 1 second. Calculate the maximum restoring torque generated in the string under undamped conditions. (π3 ≈ 31)
The maximum speed of a particle executing S.H.M. is 10 m/s and maximum acceleration is 31.4 m/s2. Its periodic time is ______
Which of the following example represent periodic motion?
A freely suspended bar magnet displaced from its N-S direction and released.
Which of the following example represent (nearly) simple harmonic motion and which represent periodic but not simple harmonic motion?
The rotation of the earth about its axis.
When two displacements represented by y1 = a sin(ωt) and y2 = b cos(ωt) are superimposed the motion is ______.
What are the two basic characteristics of a simple harmonic motion?
A person normally weighing 50 kg stands on a massless platform which oscillates up and down harmonically at a frequency of 2.0 s–1 and an amplitude 5.0 cm. A weighing machine on the platform gives the persons weight against time.
- Will there be any change in weight of the body, during the oscillation?
- If answer to part (a) is yes, what will be the maximum and minimum reading in the machine and at which position?
The time period of a simple pendulum is T inside a lift when the lift is stationary. If the lift moves upwards with an acceleration `g/2`, the time period of the pendulum will be ______.
A particle performs simple harmonic motion with a period of 2 seconds. The time taken by the particle to cover a displacement equal to half of its amplitude from the mean position is `1/a` s. The value of 'a' to the nearest integer is ______.
