Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a neat labelled circuit diagram of experimental arrangement for study of photoelectric effect.
Solution

Experimental arrangement for study of photoelectric effect.
S : monochromatic source
E : emitter electrode
C : collector electrode
G : evacuated glass tube
W : quartz window
μA : microammeter
Rh : rheostat
V : voltmeter
B : Battery
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The photoelectric work function for a metal surface is 2.3 eV. If the light of wavelength 6800A is incident on the surface of metal, find threshold frequency and incident frequency. Will there be an emission of photoelectrons or not?
[Velocity of light c = 3 x 108 m/s,
Planck’s constant, h = 6.63 * 10-34 Js ]
The photoelectric current in a photoelectric cell can be reduced to zero by a stopping potential of 1.8 volt. Monochromatic light of wavelength 2200Å is incident on the cathode. Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons in joules. [Charge on electron = 1.6 x 10-19 C]
Write three characteristic features in photoelectric effect that cannot be explained on the basis of wave theory of light, but can be explained only using Einstein's equation.
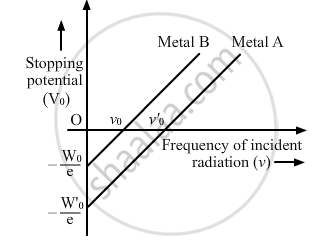
Sketch the graphs showing variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiations for two photosensitive materials A and B having threshold frequencies vA > vB.
(i) In which case is the stopping potential more and why?
(ii) Does the slope of the graph depend on the nature of the material used? Explain.
Light of intensity ‘I’ and frequency ‘v’ is incident on a photosensitive surface and causes photoelectric emission. What will be the effect on anode current when (i) the intensity of light is gradually increased. In each case, all other factors remain the same. Explain, giving justification in each case.
Light of intensity ‘I’ and frequency ‘v’ is incident on a photosensitive surface and causes photoelectric emission. What will be the effect on anode current when (ii) the frequency of incident radiation is increased. In each case, all other factors remain the same. Explain, giving justification in each case.
Light of intensity ‘I’ and frequency ‘v’ is incident on a photosensitive surface and causes photoelectric emission. What will be the effect on anode current when the anode potential is increased? In each case, all other factors remain the same. Explain, giving justification in each case.
Draw a plot showing the variation of photoelectric current versus the intensity of incident radiation on a given photosensitive surface.
The graph shows the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation for two photosensitive metals A and B. Which one of the two has higher value of work-function? Justify your answer.
If the total energy of radiation of frequency 1014 Hz is 6.63 J, calculate the number of photons in the radiation. (Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10–34 J.s.)
A photosensitive surface emits photoelectrons when red light falls on it. Will the surface emit photoelectrons when blue light is incident on it? Give reason.
Use Einstein's photoelectric equation to explain the observations from this graph ?
In photoelectric effect, why should the photoelectric current increase as the intensity of monochromatic radiation incident on a photosensitive surface is increased? Explain.
Draw a plot showing the variation of photoelectric current with collector plate potential for two different frequencies, v1 > v2, of incident radiation having the same intensity. In which case will the stopping potential be higher? Justify your answer.
What is photoelectri effect ? Defin (i) Stopping potential (ii) Photoelectric work function.
Calculate the momentum of a photon of energy 6 x I 0-19 J.
With reference to the photoelectric effect, what is meant by threshold wavelength?
State how will you use this graph to detennine the value of Planck's constant.
If the frequency of the incident radiation is increased from 4 × 1015 Hz to 8 × 1015 Hz, by how much will the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface go up?
Photoelectric effect is possible ______.
Light of wavelength 4000 Å is incident on two metals A and B. Which metal will emit photoelectrons, if their work functions are 3.8 e V and 1.6 e V respectively?
The phenomenon of photoelectric emission was observed by ______.
Consider an electron in front of metallic surface at a distance d (treated as an infinite plane surface). Assume the force of attraction by the plate is given as `1/4 q^2/(4πε_0d^2)`. Calculate work in taking the charge to an infinite distance from the plate. Taking d = 0.1 nm, find the work done in electron volts. [Such a force law is not valid for d < 0.1nm].
