Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Show variation of resistivity of Si with temperature in a graph ?
Solution
The resistivity of Silicon with temperature is shown as
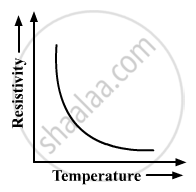
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw labelled graphs to show how electrical resistance varies with temperature for:
1) a metallic wire.
2) a piece of carbon
Consider a circuit containing an ideal battery connected to a resistor. Do "work done by the battery" and "the thermal energy developed" represent two names of the same physical quantity?
Is work done by a battery always equal to the thermal energy developed in electrical circuit? What happens if a capacitor is connected in the circuit?
As the temperature of a metallic resistor is increased, the product of its resistivity and conductivity ____________ .
The resistance of an iron wire and a copper wire at 20°C are 3.9 Ω and 4.1 Ω, respectively. At what temperature will the resistance be equal? Temperature coefficient of resistivity for iron is 5.0 × 10–3 K–1 and for copper, it is 4.0 × 10–3 K–1. Neglect any thermal expansion.
Is inversion temperature always double the neutral temperature? Does the unit of temperature have an effect in deciding this question?
An electric kettle used to prepare tea, takes 2 minutes to boil 4 cups of water (1 cup contains 200 cc of water) if the room temperature is 25°C. (a) If the cost of power consumption is Re 1.00 per unit (1 unit = 1000 watt-hour), calculate the cost of boiling 4 cups of water. (b) What will be the corresponding cost if the room temperature drops to 5°C?
A carbon resistor has coloured bands as shown in Figure 2 below. The resistance of the resistor is:
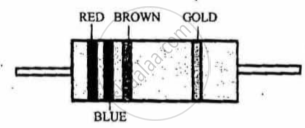
figure 2
A metallic wire has a resistance of 3.0 Ω at 0°C and 4.8 Ω at 150°C. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of its material.
