Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
Solution
In SN1 reaction, formation of carbocation as an intermediate takes place. This carbocation has sp2-hybridised and planar structure. This planar carbocation is attacked by nucleophile from both the sides equally to form d and l isomers in equal proportion. Such products are called racemic mixture. Hence, SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemisation in optically active alkyl halides.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
How do you convert the following:
Ethanol to propanenitrile
Which compound in the following pair will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH−?
CH3Br or CH3I
Which would undergo SN2 reaction faster in the following pair and why ?
CH3 – CH2 – Br and CH3 – CH2 – I
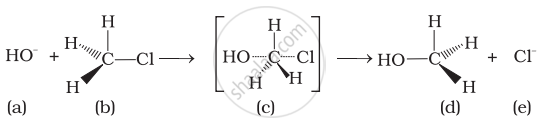
Which of the statements are correct about above reaction?
(i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles.
(ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised.
(iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C4H9Br}\] is treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another optically active isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and \[\ce{KOH}\] both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
Which one is the correct order of nucleophilic strength (pKa) of following nucleophiles?
Racemisation occurs in ______.
Complete the reaction with the main product formed:

Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
