Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
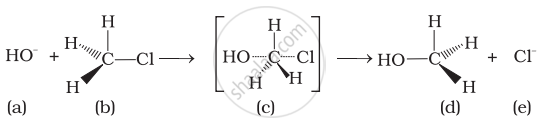
Which of the statements are correct about above reaction?
(i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles.
(ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised.
(iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
Solution
(i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles.
(iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
Explanation:
HO− and Cl− are nucleophiles.
In (iii), C atom is sp2 hybridised due to formation of \[\ce{C - OH}\] bond and breaking of \[\ce{C - Cl}\] bond simultaneously. So, in the transition state, the C atom is bonded to only 3 H atoms completely.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide?
moist silver oxide
Which of the following is an example of SN2 reaction?
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched?
| Reaction | Product | |
| I | RX + AgCN | RNC |
| II | RX + KCN | RCN |
| III | RX + KNO2 | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.......}\ce{O}\\ \phantom{.....}/\\ \ce{R - N}\phantom{....}\\ \phantom{.....}\backslash\backslash\\ \phantom{.......}\ce{O} \end{array}\] |
| IV | RX + AgNO2 | \[\ce{R-O-N=O}\] |
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for an SN2 reaction is:
Racemic compound has ____________.
Read the passage given below and answer the following question:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction of haloalkane can be conducted according to both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. However, which mechanism it is based on is related to such factors as the structure of haloalkane, and properties of leaving group, nucleophilic reagent and solvent.
Influences of halogen: No matter which mechanism the nucleophilic substitution reaction is based on, the leaving group always leave the central carbon atom with electron pair. This is just the opposite of the situation that nucleophilic reagent attacks the central carbon atom with electron pair. Therefore, the weaker the alkalinity of leaving group is, the more stable the anion formed is and it will be more easier for the leaving group to leave the central carbon atom; that is to say, the reactant is more easier to be substituted. The alkalinity order of halogen ion is I− < Br− < Cl− < F− and the order of their leaving tendency should be I− > Br− > Cl− > F−. Therefore, in four halides with the same alkyl and different halogens, the order of substitution reaction rate is RI > RBr > RCl > RF. In addition, if the leaving group is very easy to leave, many carbocation intermediates are generated in the reaction and the reaction is based on SN1 mechanism. If the leaving group is not easy to leave, the reaction is based on SN2 a mechanism.
Influences of solvent polarity: In SN1 reaction, the polarity of the system increases from the reactant to the transition state, because polar solvent has a greater stabilizing effect on the transition state than the reactant, thereby reduce activation energy and accelerate the reaction. In SN2 reaction, the polarity of the system generally does not change from the reactant to the transition state and only charge dispersion occurs. At this time, polar solvent has a great stabilizing effect on Nu than the transition state, thereby increasing activation energy and slow down the reaction rate. For example, the decomposition rate (SN1) of tertiary chlorobutane in 25℃ water (dielectric constant 79) is 300000 times faster than in ethanol (dielectric constant 24). The reaction rate (SN2) of 2-bromopropane and NaOH in ethanol containing 40% water is twice slower than in absolute ethanol. In a word, the level of solvent polarity has influence on both SN1 and SN2 reactions, but with different results. Generally speaking, weak polar solvent is favorable for SN2 reaction, while strong polar solvent is favorable for SN1 reaction, because only under the action of polar solvent can halogenated hydrocarbon dissociate into carbocation and halogen ion and solvents with a strong polarity is favorable for solvation of carbocation, increasing its stability. Generally speaking, the substitution reaction of tertiary haloalkane is based on SN1 mechanism in solvents with a strong polarity (for example, ethanol containing water).
Nucleophilic substitution will be fastest in case of ______.
Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction?
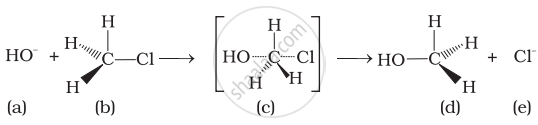
(i) The given reaction follows SN2 mechanism.
(ii) (b) and (d) have opposite configuration.
(iii) (b) and (d) have same configuration.
(iv) The given reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
When CH3CH2CHCl2 is treated NaNH2 product formed is:-
An organic compound A with the molecular formula (+) C4H9Br undergoes hydrolysis to form (+) C4H9OH. Give the structure of A and write the mechanism of the reaction.
