Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Minimise Z = – 3x + 4 y
subject to x + 2y ≤ 8, 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solution
The system of constraints is
x + 2y ≤ 8 ....(i)
3x + 2y ≤ 12 ....(ii)
and x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 ...(iii)
Let `l_1: x + 2y = 8; l_2: 3x + 2y = 12`
The shaded region in the figure is the feasible region determined by the system of constraints (i) to (iii).
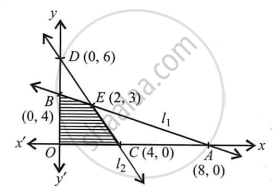
It is observed that the feasible region OCEB is bounded.
Thus, we use the Corner Point Method to determine the minimum value of Z.
We have, Z = - 3x + 4y
The co-ordinates of O, C, E and B are (0, 0), (4, 0), (2, 3)
(on solving x + 2y = 8 and 3x + 2y = 12) and (0, 4) respectively.
| Corner Point | Corresponding values of Z |
| (0, 0) | 0 |
| (4, 0) | -12 (Minimum) |
| (2, 3) | 6 |
| (0, 4) | 16 |
Hence, Zmin = -12 at the point ( 4, 0)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two tailors, A and B, earn Rs 300 and Rs 400 per day respectively. A can stitch 6 shirts and 4 pairs of trousers while B can stitch 10 shirts and 4 pairs of trousers per day. To find how many days should each of them work and if it is desired to produce at least 60 shirts and 32 pairs of trousers at a minimum labour cost, formulate this as an LPP
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Maximise Z = 3x + 4y
subject to the constraints : x + y ≤ 4, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Maximise Z = 5x + 3y
subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 15, 5x + 2y ≤ 10, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points.
Minimise and Maximise Z = 5x + 10 y
subject to x + 2y ≤ 120, x + y ≥ 60, x – 2y ≥ 0, x, y ≥ 0.
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points.
Minimise and Maximise Z = x + 2y
subject to x + 2y ≥ 100, 2x – y ≤ 0, 2x + y ≤ 200; x, y ≥ 0.
Refer to Example 9. How many packets of each food should be used to maximize the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the maximum amount of vitamin A in the diet?
If the feasible region for a linear programming problem is bounded, then the objective function Z = ax + by has both a maximum and a minimum value on R.
The minimum value of the objective function Z = ax + by in a linear programming problem always occurs at only one corner point of the feasible region
Determine the maximum value of Z = 3x + 4y if the feasible region (shaded) for a LPP is shown in Figure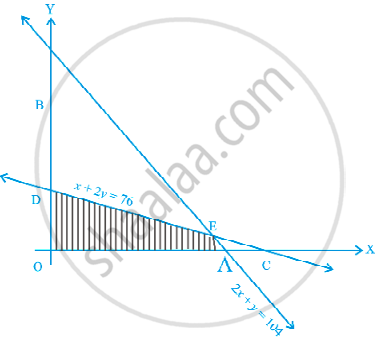
A man rides his motorcycle at the speed of 50 km/hour. He has to spend Rs 2 per km on petrol. If he rides it at a faster speed of 80 km/hour, the petrol cost increases to Rs 3 per km. He has atmost Rs 120 to spend on petrol and one hour’s time. He wishes to find the maximum distance that he can travel. Express this problem as a linear programming problem
Refer to question 15. Determine the maximum distance that the man can travel.
Refer to question 15. Determine the maximum distance that the man can travel.
In order to supplement daily diet, a person wishes to take some X and some wishes Y tablets. The contents of iron, calcium and vitamins in X and Y (in milligrams per tablet) are given as below:
| Tablets | Iron | Calcium | Vitamin |
| X | 6 | 3 | 2 |
| Y | 2 | 3 | 4 |
The person needs atleast 18 milligrams of iron, 21 milligrams of calcium and 16 milligrams of vitamin. The price of each tablet of X and Y is Rs 2 and Rs 1 respectively. How many tablets of each should the person take in order to satisfy the above requirement at the minimum cost?
A company makes 3 model of calculators: A, B and C at factory I and factory II. The company has orders for at least 6400 calculators of model A, 4000 calculator of model B and 4800 calculator of model C. At factory I, 50 calculators of model A, 50 of model B and 30 of model C are made every day; at factory II, 40 calculators of model A, 20 of model B and 40 of model C are made everyday. It costs Rs 12000 and Rs 15000 each day to operate factory I and II, respectively. Find the number of days each factory should operate to minimise the operating costs and still meet the demand.
The feasible solution for a LPP is shown in Figure. Let Z = 3x – 4y be the objective function. Minimum of Z occurs at ______.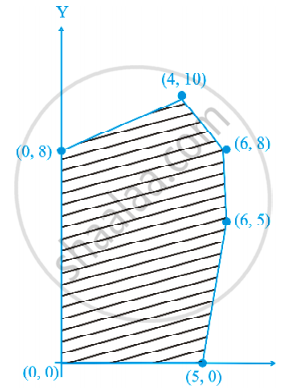
Refer to Question 32, Maximum of F – Minimum of F = ______.
In a LPP, the linear inequalities or restrictions on the variables are called ____________.
A feasible region of a system of linear inequalities is said to be ______ if it can be enclosed within a circle.
The feasible region for an LPP is always a ______ polygon.
If the feasible region for a LPP is unbounded, maximum or minimum of the objective function Z = ax + by may or may not exist.
In a LPP, the minimum value of the objective function Z = ax + by is always 0 if the origin is one of the corner point of the feasible region.
For an objective function Z = ax + by, where a, b > 0; the corner points of the feasible region determined by a set of constraints (linear inequalities) are (0, 20), (10, 10), (30, 30) and (0, 40). The condition on a and b such that the maximum Z occurs at both the points (30, 30) and (0, 40) is:
In a linear programming problem, the constraints on the decision variables x and y are x − 3y ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 0 ≤ x ≤ 3. The feasible region:
Objective function of a linear programming problem is ____________.
The maximum value of the object function Z = 5x + 10 y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 120, x + y ≥ 60, x - 2y ≥ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ____________.
In Corner point method for solving a linear programming problem, one finds the feasible region of the linear programming problem, determines its corner points, and evaluates the objective function Z = ax + by at each corner point. If M and m respectively be the largest and smallest values at corner points then ____________.
In Corner point method for solving a linear programming problem, one finds the feasible region of the linear programming problem, determines its corner points, and evaluates the objective function Z = ax + by at each corner point. Let M and m respectively be the largest and smallest values at corner points. In case the feasible region is unbounded, m is the minimum value of the objective function.
In a LPP, the objective function is always ____________.
Maximize Z = 3x + 5y, subject to x + 4y ≤ 24, 3x + y ≤ 21, x + y ≤ 9, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Maximize Z = 6x + 4y, subject to x ≤ 2, x + y ≤ 3, -2x + y ≤ 1, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Maximize Z = 10 x1 + 25 x2, subject to 0 ≤ x1 ≤ 3, 0 ≤ x2 ≤ 3, x1 + x2 ≤ 5.
Maximize Z = 10×1 + 25×2, subject to 0 ≤ x1 ≤ 3, 0 ≤ x2 ≤ 3, x1 + x2 ≤ 5.
