Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve the following problem.
Which will require more energy, heating a 2.0 kg block of lead by 30 K or heating a 4.0 kg block of copper by 5 K?
(slead = 128 J kg–1 K–1, `"s"_"copper"` = 387 J kg–1 K–1)
Solution
Given: mlead = 2 kg, ΔTlead = 30 K,
slead = 128 J/kg K,
mCu = 4 kg, ΔTCu = 5 K,
sCu = 387 J/kg K
To find: Substance requiring more heat energy.
Formula: Q = ms ΔT
Calculation: From formula,
For lead, Qlead = 2 × 128 × 30 = 7680 J
For Copper, QCu = 4 × 387 × 5 = 7740 J
QCu > Qlead, copper will require more heat energy.
Copper will require more heat energy.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
Explain the term 'steady state'.
Answer the following question.
Define coefficient of thermal conductivity.
Answer the following question.
Give any four applications of thermal conductivity in everyday life.
Answer the following question.
How heat transfer occurs through radiation in absence of a medium?
Answer the following question.
Which materials can be used as thermal insulators and why?
Solve the following problem.
The rate of flow of heat through a copper rod with temperature difference 30 °C is 1500 cal/s. Find the thermal resistance of copper rod.
Solve the following problem.
An electric kettle takes 20 minutes to heat a certain quantity of water from 0 °C to boiling point. It requires 90 minutes to turn all the water at 100 °C into steam. Find the latent heat of vaporization. (Specific heat of water = 1 cal/g °C)
Liquid is filled in a vessel which is kept in a room with temperature 20° C. When the temperature of the liquid is 80° C, then it loses heat at the rate of 90 cal/s. What will be the rate of loss of heat when the temperature of the liquid is 40° C?
If 1 g of a steam which is at 100°C starts melting then how much ice will remain at 0° C? (Latent heat of ice = 80 cal/g and latent heat of steam= 540 cal/g)
In order that the heat flows from one part of a solid to another part, what is required?
Heat energy is incident on the surface at the rate of 1000 J/min. If the coefficient of absorption is 0.8 and the coefficient of reflection is 0.1 then heat energy transmitted by the surface in 5 minutes is ______.
A slab consist of two parallel layers of copper and brass of the same thickness and having thermal conductivities in the ratio 1 : 4. If the free face of brass is at 100°C and that of copper at 0°C, the temperature of interface is ______.
A ring consisting of two parts ADB and ACB of same conductivity K carries an amount of heat H. The ADB part is now replaced with another metal keeping the temperatures T1 and T2 constant. The heat carried increases to 2H. What should be the conductivity of the new ADB part? (Given `"ACB"/"ADB"` = 3)
Two rectangular blocks A and B of different metals have same length and same area of cross-section. They are kept in such a way that their cross-sectional area touch each other. The temperature at one end of A is 100°C and that of B at the other end is 0°C. If the ratio of their thermal conductivity is 1 : 3, then under steady state, the temperature of the junction in contact will be ______.
A thin square steel plate with each side equal to 10 cm is heated by a blacksmith. The rate of radiated energy by the heated plate is 1134 watts. The temperature of the hot steel plate is ______.
(Stefan's constant σ = 5.67 × 10-8 watt m-2K-4 emissivity of the plate = 1)
An electric heater is used in a room with a total wall area of 137 m2 to maintain a temperature of +20°C inside it when the outside temperature is -10°C. The walls have three different layers of materials. The innermost layer is of wood of thickness 2.5 cm, the middle layer is of cement of thickness 1.0 cm and the outermost layer is brick of 25.0 cm. The power of the electric heater will be ______ W. Assume that there is no heat loss through the floor and the ceiling. The thermal conductivities of wood, cement, and brick are 0.125, 1.5, and 1.0 watt/m/°C respectively.
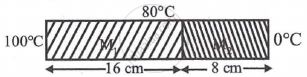
Two metallic blocks M1 and M2 of same area of cross-section are connected to each other (as shown in figure). If the thermal conductivity of M2 is K then the thermal conductivity of M1 will be ______. [Assume steady state heat conduction]
Two rods of the same material, same length and same radius transfer a given amount of heat in t second when they are joined end-to-end. When the rods are joined one above the other, then they will transfer the same heat in the same conditions in time ______.
