Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State Newton’s second law.
Solution
“The force acting on a body is directly proportional to the rate of change of linear momentum of the body and the change in momentum takes place in the direction of the force”.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A truck starts from rest and rolls down a hill with a constant acceleration. It travels a distance of 400 m in 20 s. Find its acceleration. Find the force acting on it if its mass is 7 metric tonnes (Hint: 1 metric tonne = 1000 kg).
An automobile vehicle has a mass of 1500 kg. What must be the force between the vehicle and road if the vehicle is to be stopped with a negative acceleration of 1.7 m s−2?
An object of mass 100 kg is accelerated uniformly from a velocity of 5 ms−1 to 8 ms−1 in 6 s. Calculate the initial and final momentum of the object. Also, find the magnitude of the force exerted on the object.
A hammer of mass 500 g, moving at 50 ms−1, strikes a nail. The nail stops the hammer in a very short time of 0.01 s. What is the force of the nail on the hammer?
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
Newton’s second law of motion can be written as Force = mass × _____________ or Force = _____________ of change of _____________.
A car of mass 2400 kg moving with a velocity of 20 m s-1 is stopped in 10 seconds on applying brakes. Calculate the retardation and the retarding force.
A passenger in a moving train tosses a coin which falls behind him. This shows that the motion of train is :
Which of the following situations involves the Newton's second law of motion?
Newton’s III law is applicable
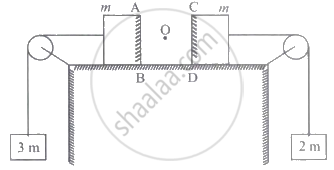
Two blocks each of mass m lie on a smooth table. They are attached to two other masses as shown in the figure. The pulleys and strings are light. An object O is kept at rest on the table. The sides AB and CD of the two blocks are plane and made reflecting. The acceleration of two images formed in those two reflecting surfaces with respect to each other is ______.