Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Study the diagram given below that represents Cu-Ag electrochemical cell and answer the questions that follow.
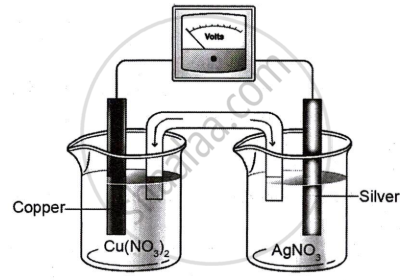
Given \[\ce{E^0_{(Cu^{2+}/Cu)}}\] = 0.337V; \[\ce{E^0_{(Ag^+/Ag)}}\] = 0.799V
- Write the cell reaction for the above cell.
- Calculate the standard emf of the cell.
- If the concentration of [Cu2+] is 0.1 M and Ecell is 0.422 V, at 25°C, calculate the concentration of [Ag+].
- Calculate ΔG for the cell.
Solution
1. Anode: \[\ce{Cu -> Cu^{2+} + 2e-}\]
Cathode: \[\ce{2Ag+ + 2e- -> 2Ag }\]
Cell reaction: \[\ce{Cu + 2Ag+ -> Cu^{2+} + 2Ag}\]
2. Standard emf \[\ce{(E°_{cell}) = E°_{cathode} - E°_{anode}}\]
= 0.799 − 0.337
= 0.462 V
3. `"E"_("cell") = "E"°_("cell") - (0.0591)/"n" log ("Cu"^(2+))/(["Ag"^+]^2)`
`0.422 = 0.462 - (0.0591)/2 log ([0.1])/(["Ag"^+]^2)`
`log ([0.1])/(["Ag"^+]^2) = ((0.462 - 0.422))/0.0591 xx 2`
= 1.35
log[0.1] − 2log[Ag+] = 1.35
−1 − 2log [Ag+] = 1.35
2log [Ag+] = −1 − 1.35 = − 2.35
log [Ag+] = −1.125
[Ag+] = 7.5 × 10−2 M
4. ΔG = −nFEcel
= − 2 × 96500 × 0.422
= 81446 J mol−1
= 81.446 kJ mol−1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets :
(zero, first, second, increased, decreased, anode, cathode, active, inactive, potassium cyanide, internal, external, dependent, independent, red, benzoic acid, benzoin, common ion effect, salt hydrolysis, alkali, potassium hydroxide,)
(i) In a galvanic cell, electrons flow from ………. to ……….. through the connecting wires.
(ii) Racemic mixtures are optical …………. because of …………… compensation.
(iii) The half-life period of a …………. order reaction is …………. of the concentration of the reactant.
(iv) Benzaldehyde when treated with an alcoholic solution of ……… forms ………..
(v) The solubility of calcium oxalate is …………. in the presence of ammonium oxalate because of ……… .
The following electrochemical cell is set up at 298 K:
`"Zn"//"Zn"^(2+)("aq")(1"M")////"Cu"^(2+)("aq")(1"M")//"Cu"`
Given`-> "E"_("Zn"^(2+)//"2n")^0 = -0.761"V", "E"_("Cu"^(2+)//"Cu")^0 = +0.339"V"`
Write the cell reaction.
The following electrochemical cell is set up at 298 K:
`"Zn"//"Zn"^(2+)("aq")(1"M")////"Cu"^(2+)("aq")(1"M")//"Cu"`
Given`-> "E"_("Zn"^(2+)//"2n")^0 = -0.761"V", "E"_("Cu"^(2+)//"Cu")^0 = +0.339"V"`
Calculate the emf and free energy change at 298 K.
What is an electrochemical series? How is it useful in predicting whether a metal can liberate hydrogen from acid or not?
Copper sulphate solution cannot be stored in a zinc pot. Why?
