Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Suppose the bob of the previous problem has a speed of 1.4 m/s when the string makes an angle of 0.20 radian with the vertical. Find the tension at this instant. You can use cos θ ≈ 1 − θ2/2 and SINθ ≈ θ for small θ.
Solution
Given:
Mass of the bob = m = 0.1 kg
Length of the circle = R = 1 m
Velocity of the bob = v = 1.4 m/s
Let T be the tension in the string when it makes an angle of 0.20 radian with the vertical.

From the free body diagram, we get :
\[T - \text{mg}\cos\theta = \frac{\text{mv}^2}{\text{R}}\]
\[\text{T} = \frac{\text{mv}^2}{\text{R}} + \text{mg} \cos\theta\]
\[\text { For small } \theta, \text {it is given that : } \]
\[\cos\theta = 1 - \frac{\theta^2}{2}\]
\[ \therefore T = \frac{0 . 1 \times (1 . 4 )^2}{1} + (0 . 1) \times 9 . 8\left( 1 - \frac{\theta^2}{2} \right)\]
\[ = 0 . 196 + 0 . 98 \times \left( 1 - \frac{\left( 0 . 2 \right)^2}{2} \right)\]
\[ = 0 . 196 + 0 . 9604\]
\[ = 1 . 156 N \approx 1 . 16 \text{ N }\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A train A runs from east to west and another train B of the same mass runs from west to east at the same speed along the equator. A presses the track with a force F1 and B presses the track with a force F2.
If the earth stop rotating, the apparent value of g on its surface will
The position vector of a particle in a circular motion about the origin sweeps out equal area in equal time. Its
(a) velocity remains constant
(b) speed remains constant
(c) acceleration remains constant
(d) tangential acceleration remains constant.
Find the acceleration of the moon with respect to the earth from the following data:
Distance between the earth and the moon = 3.85 × 105 km and the time taken by the moon to complete one revolution around the earth = 27.3 days.
A simple pendulum is suspended from the ceiling of a car taking a turn of radius 10 m at a speed of 36 km/h. Find the angle made by he string of the pendulum with the vertical if this angle does not change during the turn. Take g = 10 m/s2.
The bob of a simple pendulum of length 1 m has mass 100 g and a speed of 1.4 m/s at the lowest point in its path. Find the tension in the string at this instant.
A person stands on a spring balance at the equator. By what fraction is the balance reading less than his true weight?
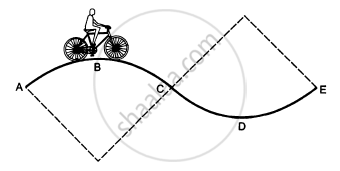
A track consists of two circular parts ABC and CDE of equal radius 100 m and joined smoothly as shown in figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing 100 kg together with the rider travels at a constant speed of 18 km/h on the track. (a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at B and at D. (b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at B, C and. (c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just before and just after the cycle crosses C. (d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take g = 10 m/s2.
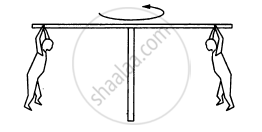
In a children's park a heavy rod is pivoted at the centre and is made to rotate about the pivot so that the rod always remains horizontal. Two kids hold the rod near the ends and thus rotate with the rod (In the following figure). Let the mass of each kid be 15 kg, the distance between the points of the rod where the two kids hold it be 3.0 m and suppose that the rod rotates at the rate of 20 revolutions per minute. Find the force of friction exerted by the rod on one of the kids.
Choose the correct option.
Select correct statement about the formula (expression) of moment of inertia (M.I.) in terms of mass M of the object and some of its distance parameter/s, such as R, L, etc.
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following cases:
(P) A planet revolving in an elliptical orbit.
(Q) A planet revolving in a circular orbit.
Principle of conservation of angular momentum comes in force in which of these?
Two particles A and B are located at distances rA and rB respectively from the centre of a rotating disc such that rA > rB. In this case, if angular velocity ω of rotation is constant, then ______
A rope is wound around a solid cylinder of mass 1 kg and radius 0.4 m. What is the angular acceleration of cylinder, if the rope is pulled with a force of 25 N? (Cylinder is rotating about its own axis.)
The real force 'F' acting on a particle of mass ' m' performing circular motion acts along the radius of circle 'r' and is directed towards the centre of circle. The square root of the magnitude of such force is (T = periodic time).
A racing car travels on a track (without banking) ABCDEFA (Figure). ABC is a circular arc of radius 2 R. CD and FA are straight paths of length R and DEF is a circular arc of radius R = 100 m. The co-efficient of friction on the road is µ = 0.1. The maximum speed of the car is 50 ms–1. Find the minimum time for completing one round.

Which of the following statements is FALSE for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed?
Define centripetal force.
