Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
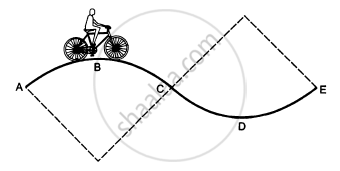
A track consists of two circular parts ABC and CDE of equal radius 100 m and joined smoothly as shown in figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing 100 kg together with the rider travels at a constant speed of 18 km/h on the track. (a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at B and at D. (b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at B, C and. (c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just before and just after the cycle crosses C. (d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take g = 10 m/s2.
Solution
Given:
Radius of the curves = r = 100 m
Mass of the cycle = m = 100 kg
Velocity = v = 18 km/hr = 5 m/s
\[(a) \text {At B}, \text {we have :} \]
\[\text{mg }- \frac{m v^2}{r} = N\]
\[ \Rightarrow N = (100 \times 10) - \left( 100 \times \frac{25}{100} \right)\]
\[ = 1000 - 25 = 975 N\]
\[\text {At D}, \text {we have : }\]
(b) At B and D, we have:
Tendency of the cycle to slide is zero.
So, at B and D, frictional force is zero.
At C, we have :
mgsinθ = f
\[\Rightarrow 1000 \times \left( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right) = 707 N\]
\[(c) \text { i Before }C, \]
\[ \text{mg}\cos\theta - N = \frac{m v^2}{r}\]
\[ \Rightarrow N = \text{mg} \cos\theta - \frac{m v^2}{r}\]
\[ = 707 - 25 = 682 N\]
ii\[\ \text{N - mg}\cos\theta = \frac{m v^2}{r}\]
\[ \Rightarrow N = \frac{m v^2}{r} + \text{mg}\cos\theta\]
\[ = 25 + 707 = 732 N\]
(d) To find the minimum coefficient of friction, we have to consider a point where N is minimum or a point just before c .
\[\text { Therefore, we have : } \]
\[\mu N = mg\sin\theta\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu \times 682 = 707\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu = 1 . 037\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A 70 kg man stands in contact against the inner wall of a hollow cylindrical drum of radius 3 m rotating about its vertical axis with 200 rev/min. The coefficient of friction between the wall and his clothing is 0.15. What is the minimum rotational speed of the cylinder to enable the man to remain stuck to the wall (without falling) when the floor is suddenly removed?
A train A runs from east to west and another train B of the same mass runs from west to east at the same speed along the equator. A presses the track with a force F1 and B presses the track with a force F2.
A simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is suspended from the ceiling of a car used in a stunt film shooting. the car moves up along an inclined cliff at a speed v and makes a jump to leave the cliff and lands at some distance. Let R be the maximum height of the car from the top of the cliff. The tension in the string when the car is in air is
Let θ denote the angular displacement of a simple pendulum oscillating in a vertical plane. If the mass of the bob is m, the tension is the string is mg cos θ
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
A particle moves in a circle of radius 1.0 cm at a speed given by v = 2.0 t where v is cm/s and t in seconds.
(a) Find the radial acceleration of the particle at t = 1 s.
(b) Find the tangential acceleration at t = 1 s.
(c) Find the magnitude of the acceleration at t = 1 s.
A mosquito is sitting on an L.P. record disc rotating on a turn table at \[33\frac{1}{3}\] revolutions per minute. The distance of the mosquito from the centre of the turn table is 10 cm. Show that the friction coefficient between the record and the mosquito is greater than π2/81. Take g =10 m/s2.
A simple pendulum is suspended from the ceiling of a car taking a turn of radius 10 m at a speed of 36 km/h. Find the angle made by he string of the pendulum with the vertical if this angle does not change during the turn. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Suppose the amplitude of a simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is θ0. Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its extreme position.
A person stands on a spring balance at the equator. By what fraction is the balance reading less than his true weight?
A turn of radius 20 m is banked for the vehicles going at a speed of 36 km/h. If the coefficient of static friction between the road and the tyre is 0.4, what are the possible speeds of a vehicle so that it neither slips down nor skids up?
What is the radius of curvature of the parabola traced out by the projectile in the previous problem at a point where the particle velocity makes an angle θ/2 with the horizontal?
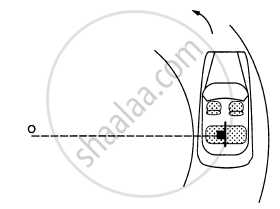
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
In a certain unit, the radius of gyration of a uniform disc about its central and transverse axis is `sqrt2.5`. Its radius of gyration about a tangent in its plane (in the same unit) must be ______.
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following cases:
(P) A planet revolving in an elliptical orbit.
(Q) A planet revolving in a circular orbit.
Principle of conservation of angular momentum comes in force in which of these?
A body is moving along a circular track of radius 100 m with velocity 20 m/s. Its tangential acceleration is 3 m/s2, then its resultant acceleration will be ______.
The centripetal force of a body moving in a circular path, if speed is made half and radius is made four times the original value, will ____________.
A body of mass m is performing a UCM in a circle of radius r with speed v. The work done by the centripetal force in moving it through `(2/3)`rd of the circular path is ______.
When a body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 45° with the horizontal, it takes time T. When the same body slides down from rest along a rough inclined plane making the same angle and through the same distance, it is seen to take time pT, where p is some number greater than 1. Calculate the co-efficient of friction between the body and the rough plane.
Define centripetal force.
