Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The bob of a simple pendulum of length 1 m has mass 100 g and a speed of 1.4 m/s at the lowest point in its path. Find the tension in the string at this instant.
Solution
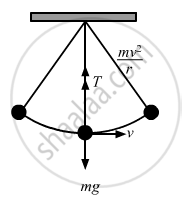
Given:
Mass of the bob = m = 100 gm = 0.1 kg
Length of the string = r = 1 m
Speed of bob at the lowest point in its path = 1.4 m/s
Let T be the tension in the string.
From the free body diagram,
we get :
\[\text{T = mg }+ \frac{\text{mv}^2}{\text{r}}\]
\[ = \left( \frac{1}{10} \right) \times 9 . 8 + \frac{(1 . 4 )^2}{10}\]
\[ = 0 . 98 + 0 . 196\]
\[ = 1 . 176 \approx 1 . 2 \text{N}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A stone of mass 0.25 kg tied to the end of a string is whirled round in a circle of radius 1.5 m with a speed of 40 rev/min in a horizontal plane. What is the tension in the string? What is the maximum speed with which the stone can be whirled around if the string can withstand a maximum tension of 200 N?
A thin circular loop of radius R rotates about its vertical diameter with an angular frequency ω. Show that a small bead on the wire loop remains at its lowermost point for `omega <= sqrt(g/R)` .What is the angle made by the radius vector joining the centre to the bead with the vertical downward direction for `omega = sqrt("2g"/R)` ?Neglect friction.
A smooth block loosely fits in a circular tube placed on a horizontal surface. The block moves in a uniform circular motion along the tube. Which wall (inner or outer) will exert a nonzero normal contact force on the block?
A particle is kept fixed on a turntable rotating uniformly. As seen from the ground the particle goes in a circle, its speed is 20 cm/s and acceleration is 20 cm/s2. The particle is now shifted to a new position to make the radius half of the original value. The new value of the speed and acceleration will be
A particle moves in a circle of radius 1.0 cm at a speed given by v = 2.0 t where v is cm/s and t in seconds.
(a) Find the radial acceleration of the particle at t = 1 s.
(b) Find the tangential acceleration at t = 1 s.
(c) Find the magnitude of the acceleration at t = 1 s.
A scooter weighing 150 kg together with its rider moving at 36 km/hr is to take a turn of a radius 30 m. What horizontal force on the scooter is needed to make the turn possible ?
A ceiling fan has a diameter (of the circle through the outer edges of the three blades) of 120 cm and rpm 1500 at full speed. Consider a particle of mass 1 g sticking at the outer end of a blade. How much force does it experience when the fan runs at full speed? Who exerts this force on the particle? How much force does the particle exert on the blade along its surface?
Suppose the bob of the previous problem has a speed of 1.4 m/s when the string makes an angle of 0.20 radian with the vertical. Find the tension at this instant. You can use cos θ ≈ 1 − θ2/2 and SINθ ≈ θ for small θ.
A person stands on a spring balance at the equator. By what fraction is the balance reading less than his true weight?
A block of mass m is kept on a horizontal ruler. The friction coefficient between the ruler and the block is μ. The ruler is fixed at one end and the block is at a distance L from the fixed end. The ruler is rotated about the fixed end in the horizontal plane through the fixed end. (a) What can the maximum angular speed be for which the block does not slip? (b) If the angular speed of the ruler is uniformly increased from zero at an angular acceleration α, at what angular speed will the block slip?
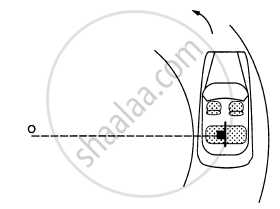
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
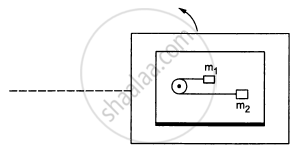
A table with smooth horizontal surface is placed in a circle of a large radius R (In the following figure). A smooth pulley of small radius is fastened to the table. Two masses m and 2m placed on the table are connected through a string going over the pulley. Initially the masses are held by a person with the string along the outward radius and then the system is released from rest (with respect to the cabin). Find the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the masses as seen from the cabin and the tension in the string.
A wheel is subjected to uniform angular acceleration about its axis. The wheel is starting from rest and it rotates through an angle θ1, in first two seconds. In the next two seconds, it rotates through an angle θ2. The ratio θ1/θ2 is ____________.
A rope is wound around a solid cylinder of mass 1 kg and radius 0.4 m. What is the angular acceleration of cylinder, if the rope is pulled with a force of 25 N? (Cylinder is rotating about its own axis.)
The centripetal force of a body moving in a circular path, if speed is made half and radius is made four times the original value, will ____________.
Angular displacement (θ) of a flywheel varies with time as θ = at + bt2 + ct3 then angular acceleration is given by ____________.
If a cyclist doubles his speed while negotiating a curve, how does the tendency to overturn vary?
An engine requires 5 seconds to go from a speed of 600 r.p.m. to 1200 r.p.m. How many revolutions does it make in this period?
A person driving a car suddenly applies the brakes on seeing a child on the road ahead. If he is not wearing seat belt, he falls forward and hits his head against the steering wheel. Why?
