Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is 1.7 m/s2. What is the time period of a simple pendulum on the surface of the moon if its time period on the surface of the earth is 3.5 s? (g on the surface of earth = 9.8 m/s2)
Solution
Given: gm = 1.7 m/s2, gE = 9.8 m/s2, TE = 3.5 s
To find: Time period on the surface of the moon (Tm)
Formula: `"T" = 2pisqrt("L"/"g")`
Calculation:
From formula,
`"T"_"m"/"T"_"E" = sqrt("g"_"E"/"g"_"m")`
∴ Tm = `sqrt(9.8/1.7) xx 3.5`
= 8.40 s
The time period of a simple pendulum on the surface of the moon is 8.40 s.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Potential energy of a particle performing linear S.H.M. is 0.1 π2x2 joule. If the mass of the particle is 20 g, find the frequency of S.H.M.
At what distance from the mean position is the kinetic energy of a particle performing S.H.M. of amplitude 8 cm, three times its potential energy?
A simple pendulum moves from one end to the other in ¼ second. What is its frequency?
A particle performing S.H.M. has velocities of 8 cm/s and 6 cm/s at displacements of 3 cm and 4 cm respectively. Calculate the amplitude and period of S.H.M.
Two wires of different materials have same length L and same diameter d. The second wire is connected at the end of the first wire and forms one single wire of double the length. This wire is subjected to stretching force F to produce the elongation l. The two wires have ______.
The total energy of the body executing S.H.M. is E. The kinetic energy of the body, when the displacement is half of the amplitude is ______.
If 'x', 'v' and 'a' denote the displacement, velocity and acceleration of a particle respectively executing SHM of periodic time t, then which one of the following does not change with time?
The equation of S.H.M. of a particle of amplitude 4 cm performing 150 oscillations per minute starting with an initial phase 30° is ____________.
The amplitude of sound is doubled and the frequency is reduced to one fourth. The intensity of sound at the same point will be ____________.
A body of mass 1 kg is suspended from a spring of negligible mass. Another body of mass 500 g moving vertically upwards hits the suspended body with a velocity 3 ms-1 and gets embedded in it. If the frequency of oscillation of the system of the two bodies after collision `10/pi` Hz, the amplitude of motion and the spring constant are respectively ____________.
A horizontal spring executes S.H.M. with amplitude 'A1', when mass 'm1' is attached to it, When it passes through mean position another mass 'm2' is placed on it. Both masses move together with amplitude 'A2'. Therefore A2 : A1 is ______
A mass M attached to a horizontal spring executes S.H.M. of amplitude A1. When the mass M passes through its mean position, then a smaller mass m is placed over it and both of them move together with amplitude A2. The ratio of `(A_1/A_2)` is ______
A mass is suspended from a vertical spring which is executing S.H.M. of frequency 5 Hz. The spring is unstretched at the highest point of oscillation. Maximum speed of the mass is ______. [acceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s2]
A particle performing SHM starts equilibrium position and its time period is 16 seconds. After 2 seconds its velocity is π m/s. Amplitude of oscillation is ______. `(cos 45° = 1/sqrt2)`
A mass m1 connected to a horizontal spring performs SHM with amplitude A. While mass m1 is passing through mean position, another mass m2 is placed on it so that both the masses move together with amplitude A1. The ratio of `"A"_1/"A"` is ______. (m2 < m1)
A sinusoidal wave travelling in the same direction have amplitudes of 3 cm and 4 cm and difference in phase by `pi/2`. The resultant amplitude of the superimposed wave is ______.
The motion of a particle varies with time according to the relation y = a sin ω t + a cos ω t. Then, ______.
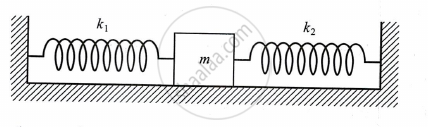
A block of mass m, connected to two springs of spring constants k1 and k2 as shown, oscillates on a smooth horizontal surface. What is the effective spring constant of the oscillation?
A particle performs linear SHM with amplitude A and frequency n. Its speed midway between an extreme position and equilibrium position is ______.
Light of a certain colour has 2500 waves to the millimetre in air. What is its frequency?
