Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The equivalent resistance between points. a and f of the network shown in Figure 2 is :
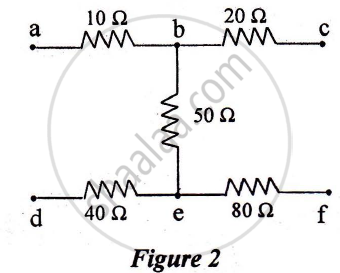
a) 24 Ω
b) 110 Ω
c) 140 Ω
d) 200 Ω
Solution
140 Ω
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two identical cells of emf 1.5 V each joined in parallel, supply energy to an external circuit consisting of two resistances of 7 Ω each joined in parallel. A very high resistance voltmeter reads the terminal voltage of cells to be 1.4 V. Calculate the internal resistance of each cell.
In a potentiometer arrangement for determining the emf of a cell, the balance point of the cell in open circuit is 350 cm. When a resistance of 9 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 300 cm. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance ‘r’ is connected across a variable resistor ‘R’. Plot a graph showing the variation of terminal potential ‘V’ with resistance R. Predict from the graph the condition under which ‘V’ becomes equal to ‘E’.
Can the potential difference across a battery be greater than its emf?
Two non-ideal batteries are connected in parallel. Consider the following statements:-
(A) The equivalent emf is smaller than either of the two emfs.
(B) The equivalent internal resistance is smaller than either of the two internal resistances.
Consider N = n1n2 identical cells, each of emf ε and internal resistance r. Suppose n1 cells are joined in series to form a line and n2 such lines are connected in parallel.
The combination drives a current in an external resistance R. (a) Find the current in the external resistance. (b) Assuming that n1 and n2 can be continuously varied, find the relation between n1, n2, R and r for which the current in R is maximum.
How many time constants will elapse before the power delivered by a battery drops to half of its maximum value in an RC circuit?
Do all thermocouples have a neutral temperature?
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across an external resistance R. Plot a graph showing the variation of P.D. across R, versus R.
