Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the reaction
\[\ce{CaCO3(s) <=> CaO(s) + CO2(g)}\] is 1.017 × 10-3 atm at 500°C. Calculate Kp at 600°C for the reaction. H for the reaction is 181 KJ mol-1 and does not change in the given range of temperature.
Solution
PCO2 = 1.017 × 10-3 atm
T = 500°C;
Kp = PCO2
∴ Kp1 = 1.017 × 10-3;
T = 500 + 273 = 773 K
Kp2 = ?
T = 600 + 273 = 873 K
∆H° = 181 KJ mol-1
`log (("K"_("P"_2))/("K"_("P"_1))) = (Delta "H"^0)/(2.303 "R") [("T"_2 - "T"_1)/("T"_2"T"_1)]`
`log (("K"_("P"_2))/(1.017 xx 10^-3)) = (181 xx 10^3)/(2.303 xx 8.314)`
`= ((873 - 773)/(873 xx 773))`
`log (("K"_("P"_2))/(1.017 xx 10^-3)) = (181 xx 10^3 xx 100)/(2.303 xx 8.314 xx 873 xx 773)`
`(("K"_("P"_2))/(1.017 xx 10^-3))` = anti log of (1. 40)
`("K"_("P"_2))/(1.017 xx 10^-3)` = 25.12
`=> "K"_("P"_2) = 25.12 xx 1.017 xx 10^-3`
`"K"_("P"_2) = 25.54 xx 10^-3`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which one of the following is incorrect statement ?
`"K"_"C"/"K"_"P"` for the reaction,
\[\ce{N2(g) + 3H2(g) <=> 2NH3(g)}\] is
In which of the following equilibrium, Kp and Kc are not equal?
For the formation of Two moles of SO3(g) from SO2 and O2, the equilibrium constant is K1. The equilibrium constant for the dissociation of one mole of SO3 into SO2 and O2 is
For a given reaction at a particular temperature, the equilibrium constant has a constant value. Is the value of Q also constant? Explain.
For the reaction, \[\ce{A2(g) + B2(g) <=> 2AB(g); \Delta H}\] is -ve.
the following molecular scenes represent differenr reaction mixture. (A-green, B-blue)
| Closed ← |
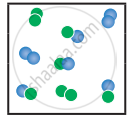 |
 |
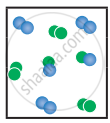 |
| System | At equilibrium | (x) | (y) |
- Calculate the equilibrium constant Kp and (Kc).
- For the reaction mixture represented by scene (x), (y) the reaction proceed in which directions?
- What is the effect of an increase in pressure for the mixture at equilibrium?
One mole of PCl5 is heated in one litre closed container. If 0.6 mole of chlorine is found at equilibrium, Calculate the value of equilibrium constant.
For the reaction
\[\ce{SrCO3(s) <=> SrO(s) + CO2(g)}\]
the value of equilibrium constant Kp = 2.2 × 10-4 at 1002 K. Calculate Kc for the reaction.
1 mol of CH4, 1 mole of CS2 and 2 mol of H2S are 2 mol of H2 are mixed in a 500 ml flask. The equilibrium constant for the reaction Kc = 4 x 10-2 mol2 lit-2. In which direction will the reaction proceed to reach equilibrium?
At particular temperature Kc = 4 × 10-2 for the reaction, \[\ce{H2S (g) <=> H2(g) +1/2 S2(g)}\]. Calculate the Kc for the following reaction.
\[\ce{3H2S (g) <=> 3H2 (g) + 3/2 S2 (g)}\]
